Chmod Linux
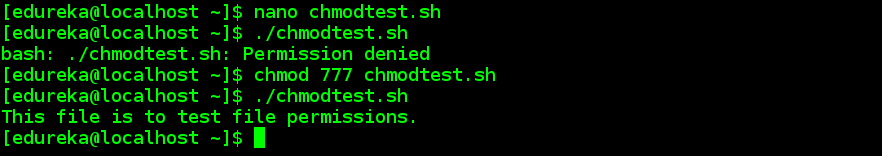
There are two ways to run the bash file.

Chmod linux. Chmod - Unix, Linux Command - chmod - To change access permissions, change mode. The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file.
Chmod 775 /opt/lampp/htdocs Is there a way to set chmod 755 for /opt/lampp/htdocs and all of its content including subfolders and files?. Chmod command in Linux What is chmod?. Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission.
Chmod clears the set-group-ID bit of a regular file if the file's group ID does not match the user's effective group ID or one of the user's supplementary group IDs, unless the user has appropriate privileges. Linux chmod command is used to change the access permissions of files and directories. In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories).
The owner can read, write and execute. Multi-user systems, such as Linux, require setting up and managing file permissions that ensure only authorized users have access to files they are supposed to. These flags are called file permissions or modes, as in "mode of access." The command name chmod stands for "change mode." It restricts the way a file can be accessed.
Using octal value & position:. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. The chmod command is used to change the file or directory access permissions.
It is dangerous to operate recursively on '/' chmod:. To combine these, just add the numbers together:. Chmod command is used in two ways :.
How to use chmod?. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System. (G)roup can read, can't write and can execute.
It stands for change mode. Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions. Linux - Solution 1:.
The first one is by using the bash command and the. The chmod command with the -R options allows you to recursively change the file’s permissions. In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership.
Chmod stands for change mode. How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux. How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command.
READ NEXT › How to Turn On Handwashing Detection on the Apple Watch. If you are new to Linux, and are looking for a way to change file/directory permissions through the command line, you'll be glad to know there exists a command - dubbed chmod - that lets you easily do this. With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linux-based distros.
$ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions. $ chmod g+x app.sh Change File Mode For Other.
$ chmod o+x app.sh Change File Mode For All. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. There will be a Permission tab where you can change the file permissions.
# alias chmod='chmod --preserve-root' and also add this to your /etc/bashrc or individual user's .bashrc file for permanent changes. This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level …. We have already described the Linux file permissions.
To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules. In this tutorial, I am going through the steps to create a bash script and to make the script executable using the chmod command. 777 where first digit is for user, second is for group and 3 rd is for others.
This is a dangerous permission to have on any file and you should avoid using it. How to set chmod for a folder and all of its subfolders and files in Linux Ubuntu Terminal ?. Finally, to run the script we need to make it executable and that can be done by using the chmod command – chmod +x cointoss.sh.
The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. To read, write and execute. Here are some command chmod commands with their explanation:.
The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation. In Linux, you can easily change the file permissions by right-clicking the file or folder and select “Properties”. The basic syntax is:.
Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix. Sudo chmod u+w myfolder to add the write permission to the username user. A plus (+) symbol adds a permission, and a minus (-) symbol removes a permission.
Therefore, Joe can access any file, of which he knows the name, in Fred's home directory. Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:. Even, it ignores the symbolic links come across recursive directory traversal.
This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person. The OP here (last seen 14) wanted to write and run something similar to a batch file.
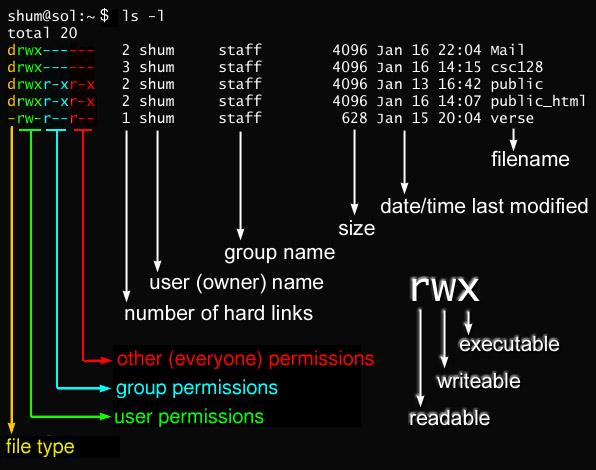
Following is a sample of ls -l command output. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. Chmod has two operating modes:.
Chmod -R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree. The name is an abbreviation of change mode. The name speaks for itself.
Chmod 0 file - Write by group chmod 002 file - Write by world chmod 100 file - execute by owner chmod 010 file - execute by group chmod 001 file - execute by world. Sudo usermod -a -G groupname username and then execute. It’s usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux system.
NAME top chmod, fchmodat — change mode of a file relative to directory file descriptor. In this article, you will learn how to change permissions of any file or directory with chmod command. Chmod doesn't really apply to those OSes and "batch file" was in scare quotes.
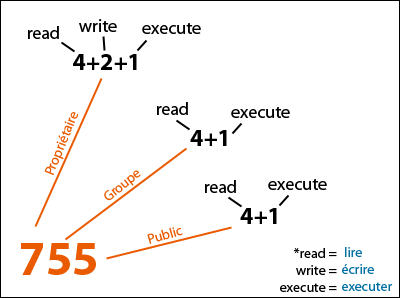
By issuing these commands, you can change groups of files and directories in Linux. Sets the permission for owner, group and others with octal values , 4 for read , 2 for write , 1 for execute and. 15-05-19 In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file.
The request is filtered by the umask. Additional restrictions may cause the set-user-ID and set-group-ID bits of MODE or RFILE to be ignored. Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits.
You can read chmod u+r as "user plus read," as it gives the user read permission. Common chmod commands and their meaning. The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories.
Chmod 755 Chmod 755 (chmod a+rwx,g-w,o-w) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute. It takes the following syntax:. Unlike in Unix-like OSes, Windows (and DOS) users don't have to use anything like chmod +x to make it so they can launch their scripts the same way they launch executable binaries.
There are three sets of permissions. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others. What is chmod ?.
But if you want to add this user to the group associated with "myfolder", you can run. CHMOD is listed in the World's largest and most authoritative dictionary database of abbreviations and acronyms The Free Dictionary. It can not change the permission of symbolic links.
The Linux implementation of this interface may differ (consult the corresponding Linux manual page for details of Linux behavior), or the interface may not be implemented on Linux. The name is an abbreviation of change mode. To know about the access permissions of a file or directory, use the ls -l command as shown below:.
On Unix-like systems, chmod is a system-level command that stands for "change mode" and allows you to manually change the permission settings of a file. Users can simply modify file permissions using the chmod (change mode) command. On Unix-like operating systems, a set of flags associated with each file determines who can access that file, and how they can access it.
Chmod command in UNIX and Linux allows modifying permissions not just on text format which is more readable but also on numeric format where combination of permissions are represented in octal format e.g. As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory. It is also used to change special mode flags.
Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. In some cases we can see the +x without a definition.
$ ./cointoss.sh TAILS $ ./cointoss.sh HEADS $ ./cointoss.sh HEADS $ ./cointoss.sh TAILS. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. Vijay Bhaskar 10/10/12 1 Comments Chmod (change mode) is one of the most frequently used commands in unix or linux operating system.
Chmod go+x ~ This command changes the mode of Fred's home directory (represented by the ~), giving permission to all users to get to files in that directory. In Linux/Unix like operating system, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. I would like to change permissions of a folder and all its sub folders and files in one step (command) in Linux.
This command is used for changing the mode of access. And, Linux is an Extensionless system. This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories.
Sudo chmod g+w myfolder to add the write permission to the group. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command. Use --no-preserve-root to override this failsafe Linux Permissions Syntax.
Using symbols (alphanumerical characters) using the octal notation method. We can enable the execution right of the all users in a file with o like below. In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users.
Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions. Not to be confused with chown , which is another system-level command on Unix-like systems that stands for "change owner" and lets you assign ownership of a file to another user, or chgrp. In this tutorial, we will discuss the basics of this command as well as provide examples explaining how it can be used in various scenarios.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 655 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-w,o-w) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. Others is special group which covers all users in a Linux system. It is one of the most used and important commands in the set of Linux security commands.
But in Linux, ownership is a massive part of file security, with file permissions providing the remainder of it. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. To recursively set permissions of files based on their type, use chmod in combination with the find command.
If you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command. Now if you write down 1 st digit in binary format it will be written as 111 on which 1 st digit is for read. It is used to change the permission for files and folders.
Use the chown and chmod commands to secure file access on your system. In short, “chmod 777” means making the file readable, writable and executable. This means that owner, group and everyone has the all the rights i.e.
The command is usually used together with a set of octal notations or alphabetical characters. Linux chmod command is used to change access permissions of files and directories. You can pass more than one file or directory.
These permissions are given to file/folder to provide a secure environment to the OS, efficient management of a file and high-level access to the users accessing the files/ folders. (O)thers can read, can't write and can execute. Now if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod -c --recursive 755 / chmod:.
Looking for online definition of CHMOD or what CHMOD stands for?. I have already tried the below command but it works only for the mentioned folder:. After that, you will be able to run it without using the sh or bash commands.
Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone. Linux File Permission :.
Chmod Modifies File Permissions In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions. Chmod ( Change Mode ) is a command line utility in Unix , Linux and other Unix like systems to change the read, write, execute permissions of a file for owner , group and others. This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command to change the access permissions of files and directories.
The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe. Chmod 444 file - Allow read permission to owner and group and world chmod 777 file - Allow everyone to read, write, and execute. Chmod command in Linux with examples Last Updated:.
The chmod command modifies the permission mode of objects in the system. In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod.

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners
Linux Commands Most Important Linux Commands Edureka

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux
Chmod Linux のギャラリー

Linux Chmod Command Dracula Servers Tutorials

The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrjnvlxj0s Bjlyqdmcffgnaicqwuoecwomv8yezuw Usqp Cau

14 04 Chmod Not Working In A Non Super User Ask Ubuntu
Linux And Unix Chmod Command Knowledge Hub

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Chmod Permission Denied Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Make Them Executable On Linux Chmod X By Erdem Sahin Medium
Solved This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Use Chegg Com

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub

Linux And Unix Chown And Chmod Command Security Problem Illustrated Nixcraft

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx
Mydiamo Guide Installation On Linux
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
Understanding Linux File Permissions And Using Chmod Pen Testing

How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Network World

How To Use The Chmod Terminal Command In Ubuntu Linux Operating Systems Wonderhowto
What To Do When You Can T Chmod Chmod Knowledgeacademy Io
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
Modify File Permissions Linux

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Linux Commands Chmod

Unix Linux Command Chmod Linux Concept
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs9h1s9aymhgxuiwaruv5svj Iw49oju6dx0zyl3syy0y4ft3ya Usqp Cau

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chown And Chmod Command Usage In Linux System Develop Paper

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Video Linux File Permissions Chmod And Chown Linux Org
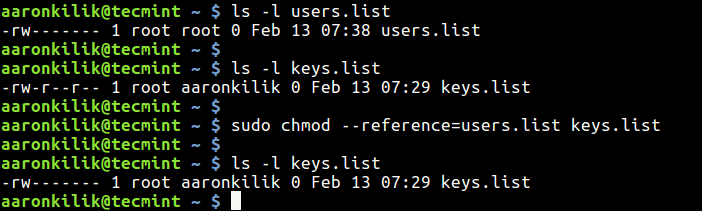
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Designlinux

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Lock Usb Devices With Chmod Command In Linux Tutorials

Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux Summary Networks

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Command Line I Can T Change Mode For Some Directories Using Chmod Ask Ubuntu

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
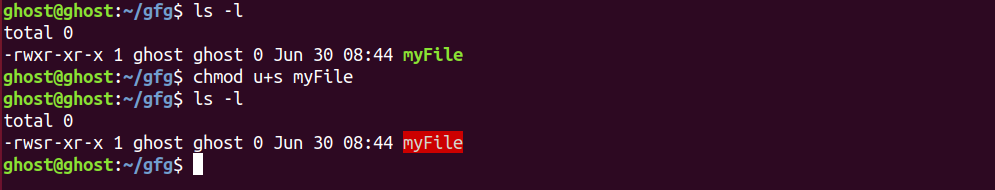
Advance File Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium

Linux Admin 101 File Permissions With Chmod Chgrp And Chown Trash Computer
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Linux Permissions Posix Chmod Chown Chgrp Youtube
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux
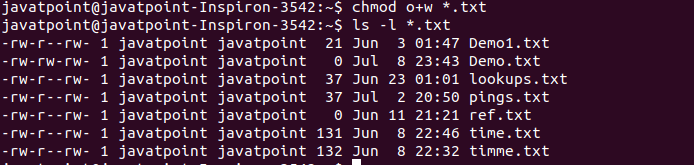
Linux Chmod Command Javatpoint
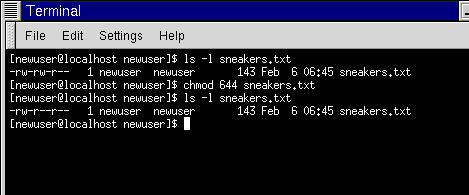
Fun With Numbers In Chmod

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
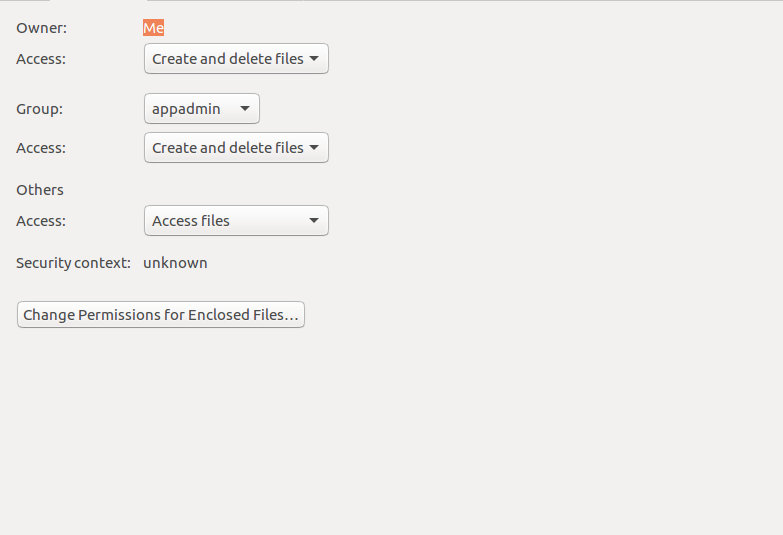
Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way

Chmod File Permissions In Linux Unix

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Whatever You Knew About Chmod Is Wrong Alien Coders

9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Chmod Wikipedia

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

Linux Chapter 3 Permission Management Commands Change File Permissions Chmod 777 Root A Programmer Sought
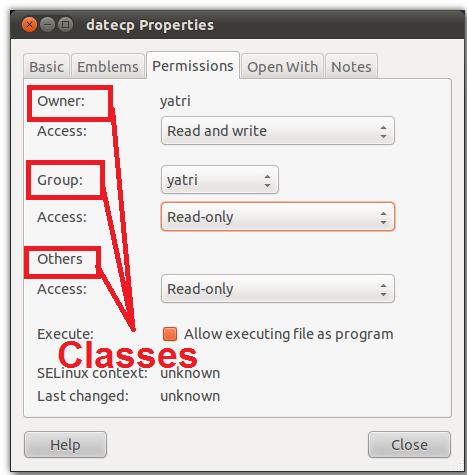
What Is Chmod 777

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
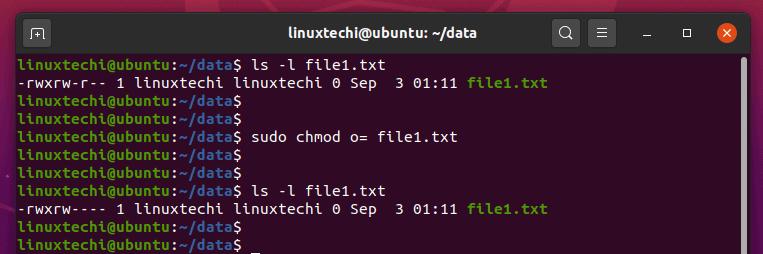
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks

Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

File Permissions Linuxhowto Net
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau
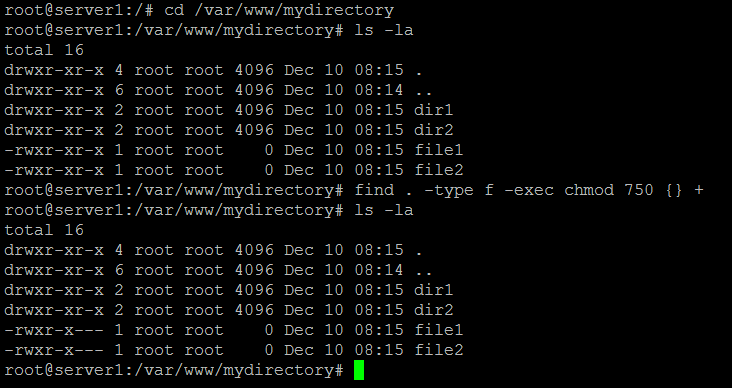
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Chmod Or File Permissions Code Blog Perlubantuan Portal




