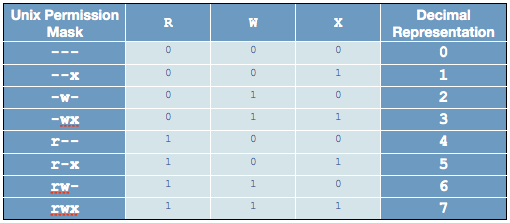
Linux Chmod Table
When you change permissions by using the absolute mode, represent permissions for each triplet by an octal mode number.
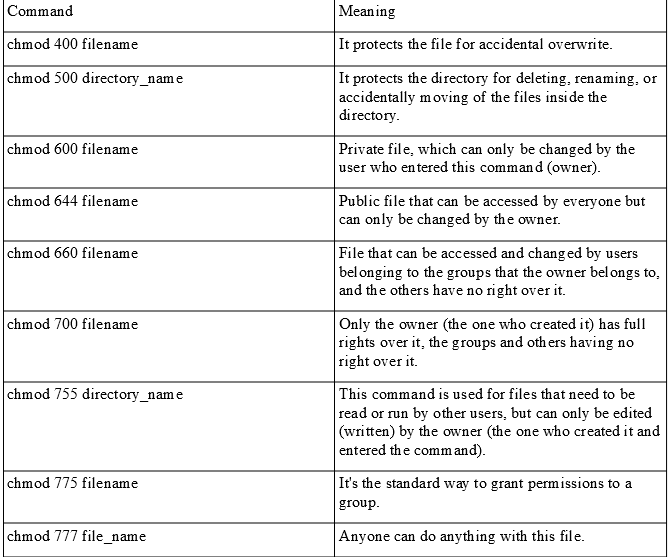
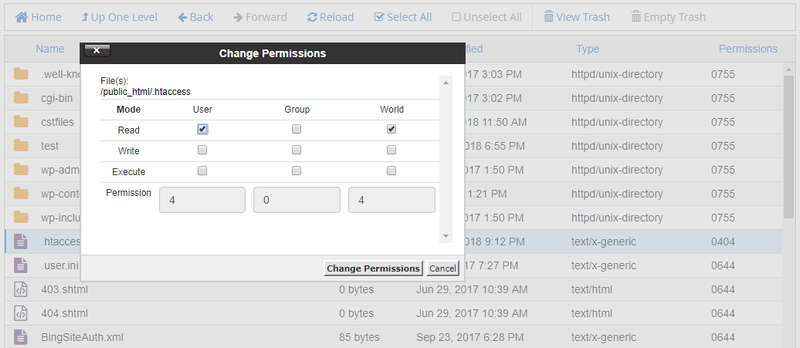
Linux chmod table. This command will do the trick:. Chmod all files to 644;. Chmod all directories with directory listing (.htaccess Options +Indexes) to 755;.
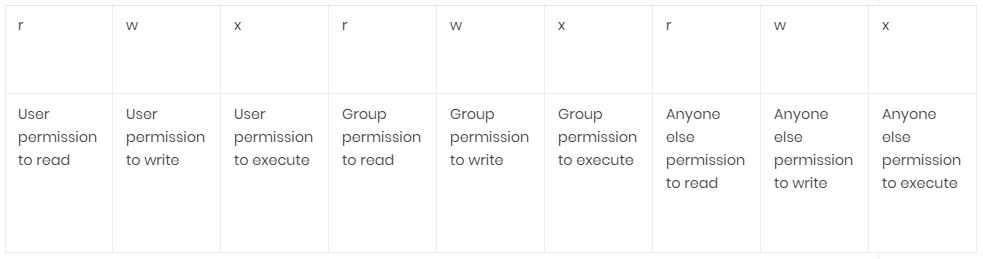
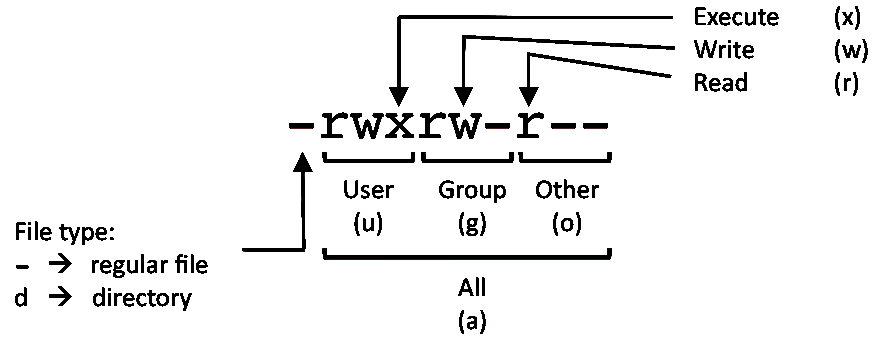
Members of your g roup can r ead and e x ecute it;. The references are used to distinguish the users to whom the permissions apply i.e. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images.
$ chmod a+r sample.txt Make a file readable and writable by the group and others. The chmod command is used to alter the permissions of a file. PERMISSION COMMAND U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx r-x chmod 775 filename rwx r-x r-x chmod 755 filename rw- rw- r-- chmod 664 filename rw- r-- r-- chmod 644 filename U = User G = Group W = World r = Readable w = writable x = executable - = no permission.
Linux - Solution 1:. O thers may only r ead it. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command.
In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command. You can use the chmod command to set permissions in either of two modes:. For example, to add execute permissions for the owner of a file you would run:.
Chmod 775 /opt/lampp/htdocs Is there a way to set chmod 755 for /opt/lampp/htdocs and all of its content including subfolders and files?. This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options. Chmod has two operating modes:.
Find /opt/lampp/htdocs -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;. File group, and others, in that order. The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod.
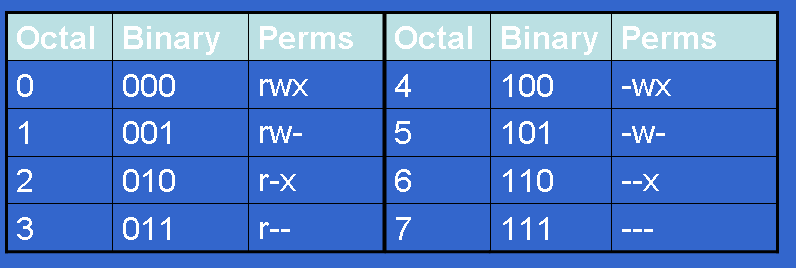
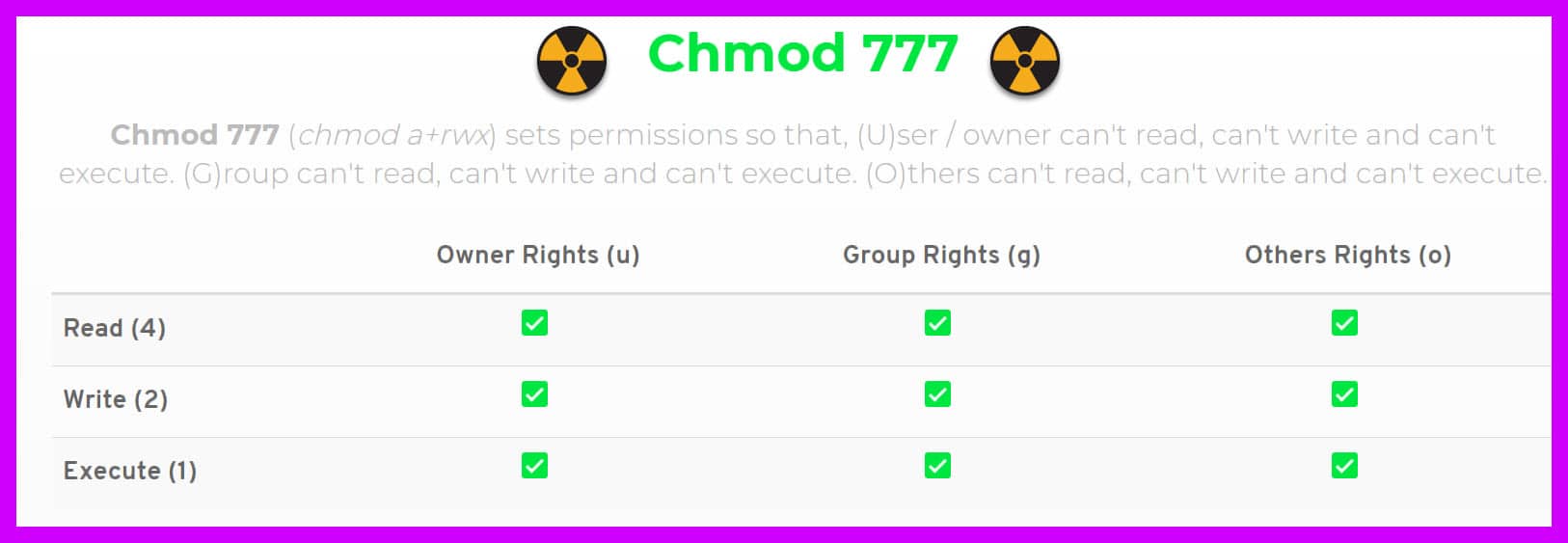
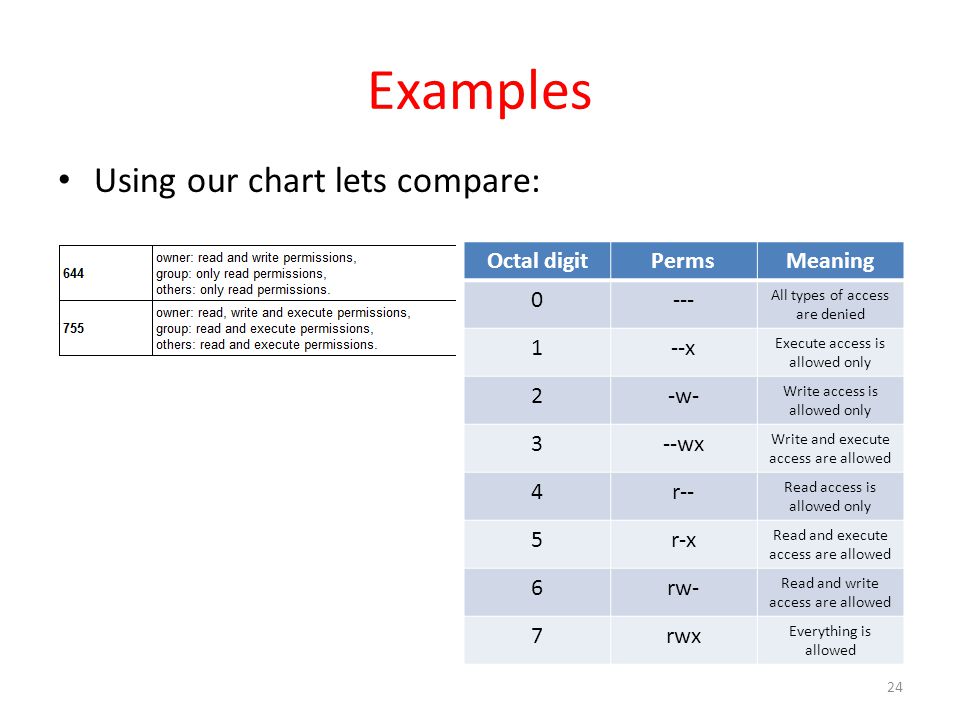
Chmod command is used to change the permissions of files and directories in Linux. Table of Contents Sooner or later in the Linux world, you will have to change the permission on a file or directory. 777 = rwxrwxrwx 755 = rwxr-xr-x 644 = rw-r--r-- 700 = rwx----- 750 = rwxr-x---.
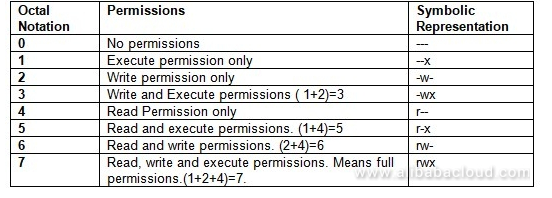
Permissions used to be called mode of access and hence chmod was the short form of change the mode of access. This example uses symbolic permissions notation. Absolute Mode - Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method most commonly used to set permissions).
The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others. There are two ways to use the chmod command:. We use the chmod command to do this, and eventually to chmod has become an almost acceptable English verb, meaning the changing of the access mode of a file.
Specifies the file or directory. We should note that many Linux security configurations will prevent keys in the .ssh folder from being used to allow SSH access if they do not have the correct permissions applied. I have created a directory /tmp/marketing on which I will apply linux sticky bit special permission # mkdir /tmp/marketing.
Who is specified as. Click below button to copy the code. There are three sets of permissions.
Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples. The below table shows some examples of permission with a numeric value and text value you can set permission either numeric or text format. Group – The Group permissions apply only to the group that has been assigned to the file or directory, they will not effect the actions of other users.
Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits. I would like to change permissions of a folder and all its sub folders and files in one step (command) in Linux. Only the current owner or superuser can use the chmod command to change file permissions on a file or directory.
This is done with the chmod command. Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions. The command is usually used together with a set of octal notations or alphabetical characters to change file permissions.
Chmod all .htaccess files to 644 chmod all robots.txt files to 644;. Linux-jwc3:/ # ls -l myfile.txt. The following command.
Linux Permissions are a great set of rules which. In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user’s file system. Chmod options mode filename filename1… chmod options mode directory_name.
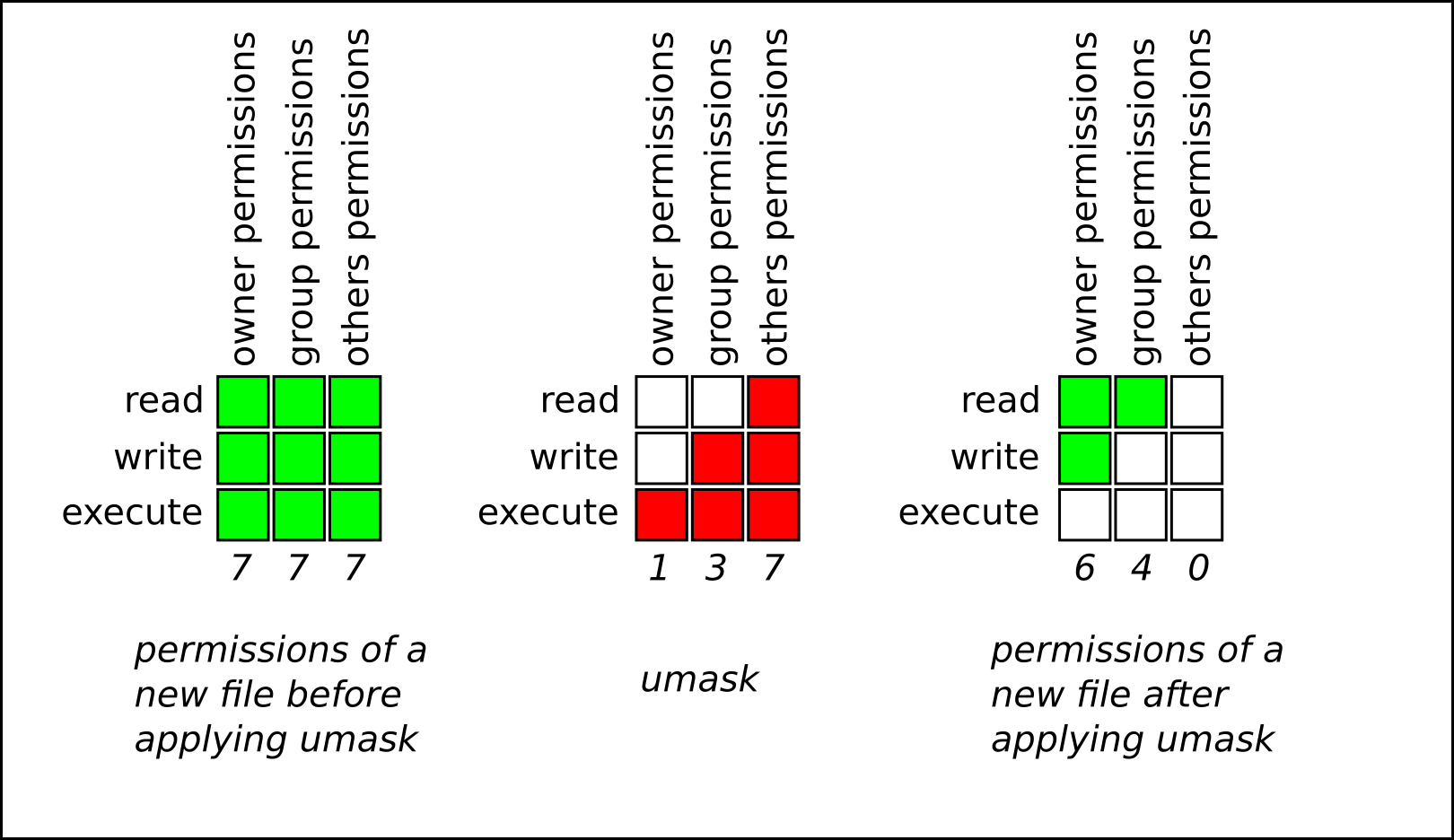
You must be superuser or the owner of a file or directory to change its permissions. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. The bits in the mask may be changed by invoking the umask command.
Chmod -R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree. Chmod all directories that users can upload files to, to 755 (ex:. The command is relatively simple to use and involves using.
See Table 15–5 for the list of valid octal values. To apply sticky bit with 755 permission # chmod 1 755 marketing/ As you see now we have "t" shown in the "execute field. It’s usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux system.
Following is a sample of ls -l command output. Additionally server-side languages provide functions that are roughly analogous to chmod in terms of operation using absolute notation. Numeric Method # The syntax of the chmod command when using numeric method has the following format:.
How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. You can use the find command. Permissions on a Linux system can be managed by using three commands:.
Linux-jwc3:/ # chmod 400 myfile.txt. CHMOD Permissions Reference Chart. $ chmod u+x samplescript.sh Allow everyone to read, write, and execute the file and turn on the set group-ID.
By David · September 18, 12. Chmod is a UNIX and Linux command for setting file or directory permissions. Add the file’s owner permissions to the permissions that the members of the file’s group have:.
In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. There are two ways to use chmod — the symbolic mode and the absolute mode. In this article, I’ll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command.
User Group Other Read 4 4 4 Write 2 2 2 Execute 1 1 1 U G O X X X Chmods:. In this article, I will take you through 11 Popular Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions. Chmod stands for “Change Mode” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system.
Change file permissions in Linux. Owner – The Owner permissions apply only the owner of the file or directory, they will not impact the actions of other users.;. You can use chmod command for changing the permissions on a file in Linux.
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules. Umask or file mode creation mask is a grouping of bits, each of which restricts how its corresponding permission is set for newly created files or directories.
It will also briefly cover the chmod command as an associated permissions tool. This guide will explain the basics of Linux permissions, and will demonstrate the usefulness of configuring umask correctly. 777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g.
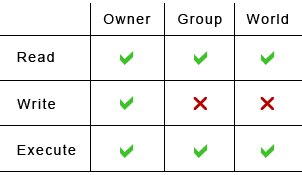
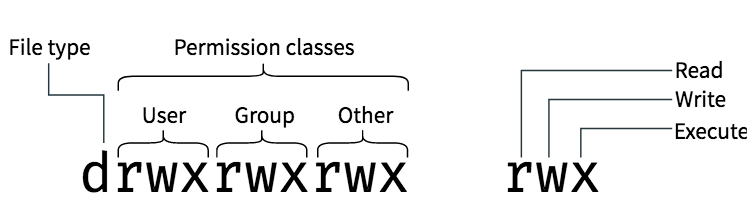
Each file and directory has three user based permission groups:. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else.
Chmod, chown and chgrp. Those commands respectively change the permissions of a file, change the owner of a file or change the group of a file. Chmod Modifies File Permissions In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions.
It may be used to add or remove permissions symbolically. For more advanced trainees it can be a desktop reference, and a collection of the base knowledge needed to proceed with system and network administration. To change the file or the directory permissions, you use the chmod (change mode) command.
I have already tried the below command but it works only for the mentioned folder:. How to change file permissions using chmod and chown. There are three different possible user levels, each with three different possible settings.
Here's a summary that I have gathered. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats.
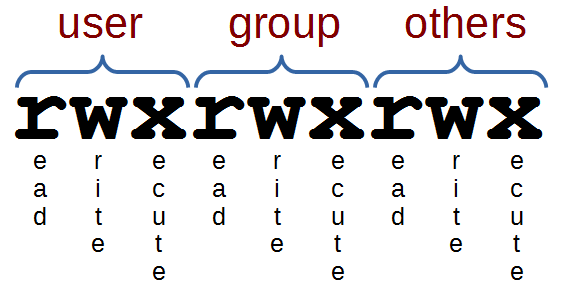
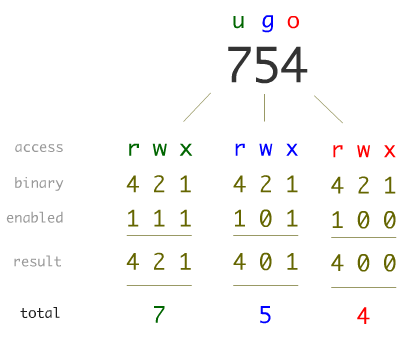
The chmod command enables you to change the permissions on a file. The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits. The letters u, g, and o stand for " user ", " group ", and " other ".
This is how I remember permissions and most likely, it will help you remember it as well. The chmod command A normal consequence of applying strict file permissions, and sometimes a nuisance, is that access rights will need to be changed for all kinds of reasons. Make a Script Executable.
$ chmod go+rw sample.txt Make a shell script executable by the user/owner. The name is an abbreviation of change mode. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 655 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-w,o-w) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily.
To change all the directories to 755 (drwxr-xr-x):. You can set read permission to the owner. The three user levels are Owner, Group, and Other.
Below are some examples to apply linux sticky bit using the Octal method with chmod in Linux and Unix. This guide was created as an overview of the Linux Operating System, geared toward new users as an exploration tour and getting started guide, with exercises at the end of each chapter. See this short guide for a crash course on permissions in Linux.
We can use chmod and chown to manipulate the file permission. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 600 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-rwx,o-rwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. $ chmod =rwx,g+s samplescript.sh Print.
$ sudo chmod 333 rainbow $ ls -l rainbow --wx-wx-wx 1 pixie zanna 0 May 24 10:09 rainbow Since the permission bits are set separately for owner, group and others, you can control file permissions for different users by combining chown and chmod. The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux.
Using chmod in Symbolic Mode. Let’s play through various conditions so that we can master basic chmod commands which can make our everyday life easier with Ubuntu. The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
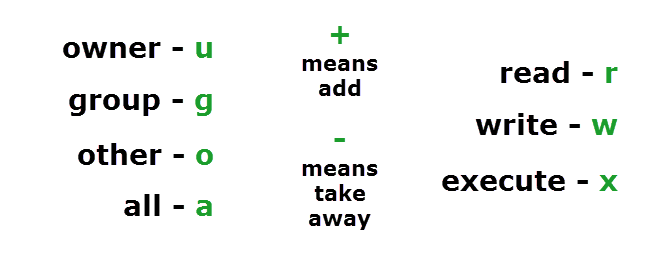
Add a sticky bit to a given directory:. Now all you have to do is think of what permissions you want, add the values associated with the permissions, and type chmod followed by the total and file or directory name. Who the permissions apply to, how the permissions are set and which permissions to set.
The “mode” consists of three parts:. The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others. By - Linux tutorial - team.
The owner of the file/directory can read and. Select the permissions you require below. Chmod.(change mode) is a widely used command to change the permissions of files and directories.It allows the setting of user, group and other bits which each define what rights each classification of user has over the files.
The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. Chmod all directories to 711;. They are list of letters that specifies whom to give permissions.
Linux is a clone of UNIX, the multi-user operating system which can be accessed by many users simultaneously.Linux can also be used in mainframes and servers without any modifications. But this raises security concerns as an unsolicited or malign user can corrupt, change or remove crucial data.For effective security, Linux divides authorization into 2 levels. The easiest way for a beginner to modify file or directory permissions is to use the symbolic mode.
It allows the permissions to be changed in either Symbolic form or in numerical form. Numeric format example of permission in Linux using chmod. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions.
It is a confusing topic until you learn it, but it is needed if you plan to work with UNIX or Linux web servers. If the mask has a bit set to "1", it means the corresponding initial file permission will be disabled.A bit set to "0" in the mask means that the corresponding.

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Shell Tutorial Part 9 Changing Permissions Youtube
Linux Chmod Table のギャラリー
Read Just Enough Linux Leanpub

Umask Sharing Is Caring
Chmod Directory Read Write And Type
How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
Controlling File Permissions With Umask
How To Use Unix File Permissions To Increase Security Developer Drive

An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean
How Do I Set File Permissions For Files Scripts Or Directories Linux Accounts Only

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs
Solved This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Use Chegg Com

Chmod Wikipedia

Linux Command Line Cheat Sheet Kalitut
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau

ल नक स म Chmod कम ड क य ह Computer Hindi Notes
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux Guide To Linux Certification Second Edition Ppt Video Online Download
Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask

System Integrity Using Files Permissions Processes Root And Sudo Teklimbu S Weblog

Linux User Group And File Permission Introduction

Changing Permissions On A File In Linux Mvps Net Blog Mvps Net Tutorials
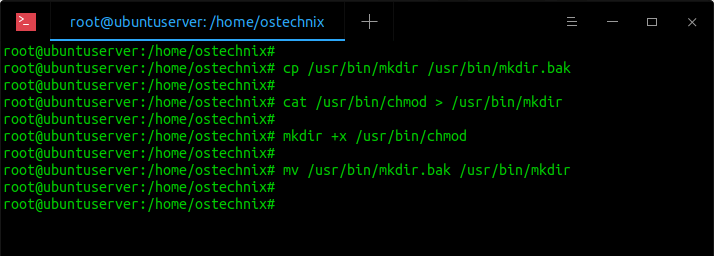
Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
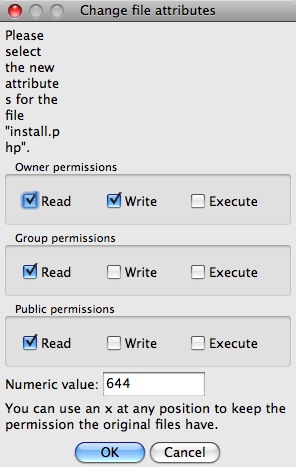
Linux Chmod How To Make A Perl Script Executable Alvinalexander Com

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu

14 Permission And Modification Times

0xax Reading Writing Cheat Sheets Cheating
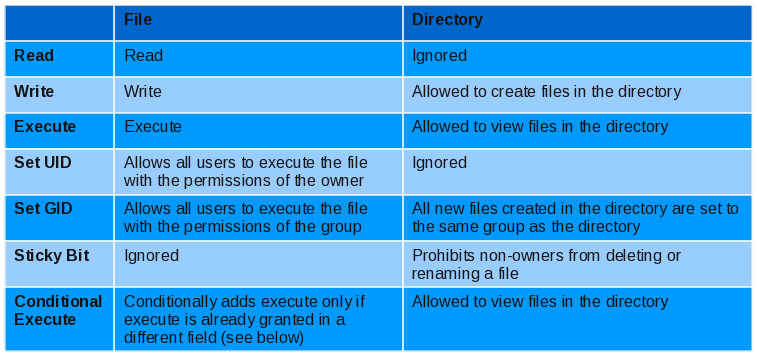
Unix Linux Filesystem Permissions 101

Chmod X Explained Everything You Need To Know
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
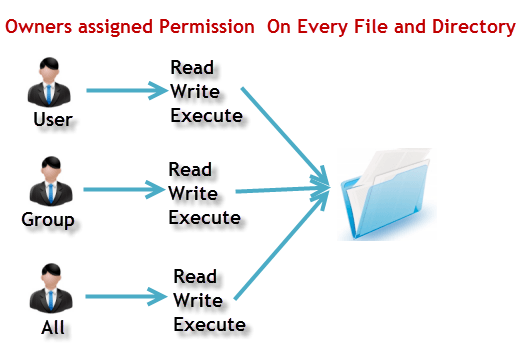
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Setting File And Directory Access Permissions Plesk Obsidian Documentation

File Chmod Infographic 001 Png Linux Help

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

File Permissions Suid Sgid Sticky Bit Acl Nmcli Ssh And Nmtui Tools For Rhcsa Unixmen

Chmod 555

Special Permissions Access Control Filesystem Attributes In Linux Study Com
Linux Permissions Tables Reffffference

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Understanding File Permissions

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Basic Linux Commands Gooribi Inc

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Can We Set File Permissions To 775 By Using Umask In Linux If Yes What Would The Umask Be And How Will It Be Calculated Quora

Lpt Memorize Chmod Values By Using A Truth Table Imgur

Chmod Change Permissions To A Specific User In Ubuntu 12 04 Ask Ubuntu

Top 48 Linux Interview Questions Answers Updated

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
Linux Permissions Explained Linux Hint
Linux Chmod Tips
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux For Beginners Part 6 Understanding File Permission And Ownership
Chapter 5 Managing File Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Red Hat Customer Portal

Unix Commands Changing Permissions Dreamhost Knowledge Base
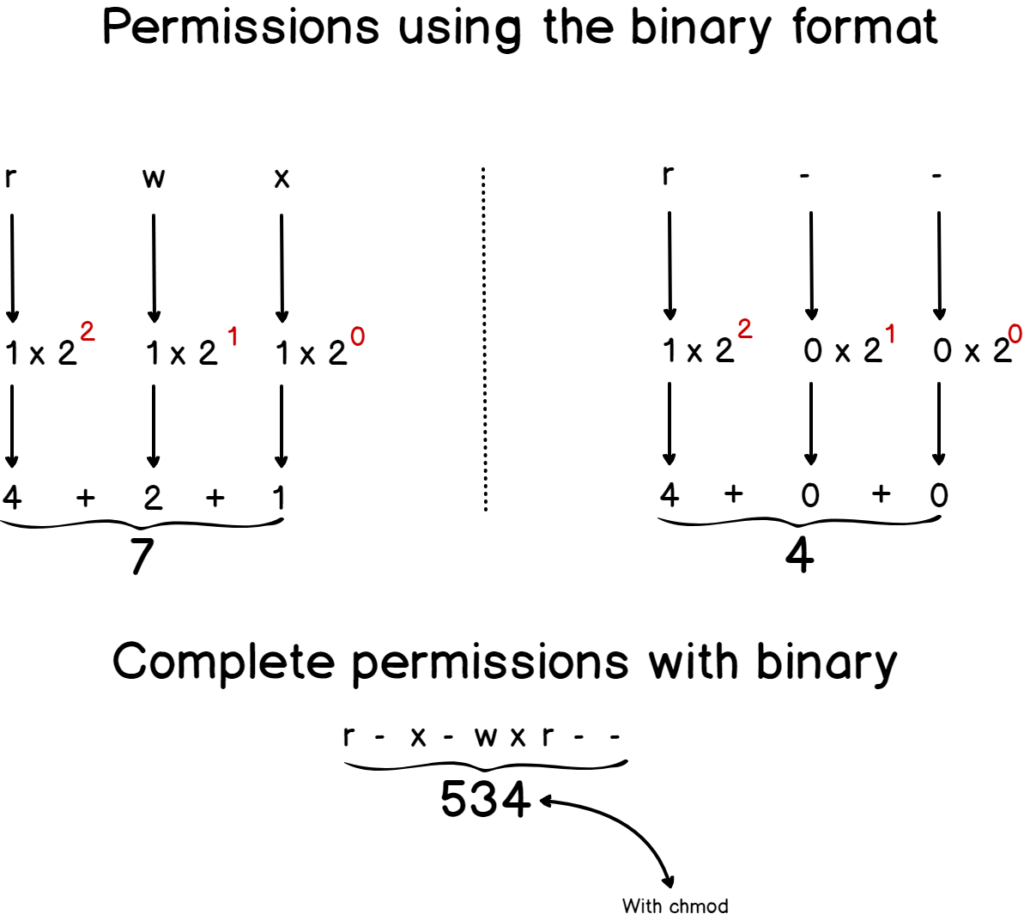
Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

File Permissions Suid Sgid Sticky Bit Acl Nmcli Ssh And Nmtui Tools For Rhcsa Unixmen

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders
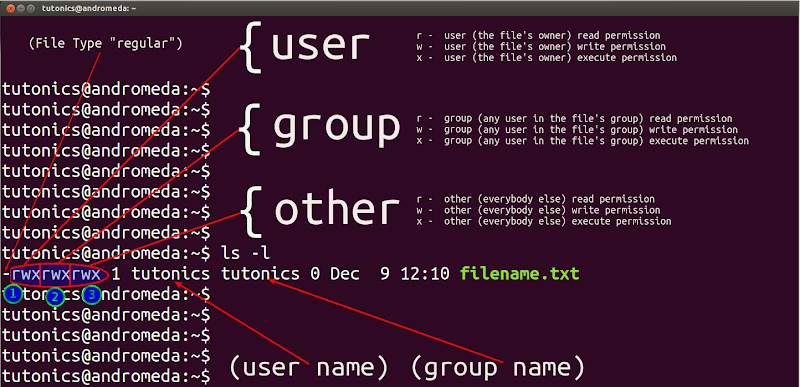
Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics

File Permission Meanings Stack Overflow

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
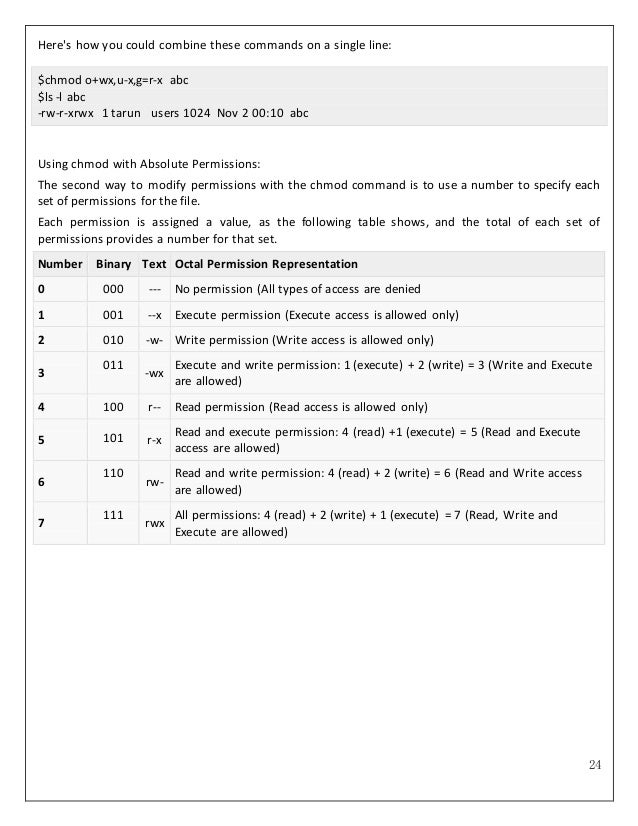
Srgoc Linux

File Permissions Linuxhowto Net
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq2oq90gyu7qjtwwppsiodhgqotjbz3awrstnhczkm6hwgdiahx Usqp Cau

Unix Permissions

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
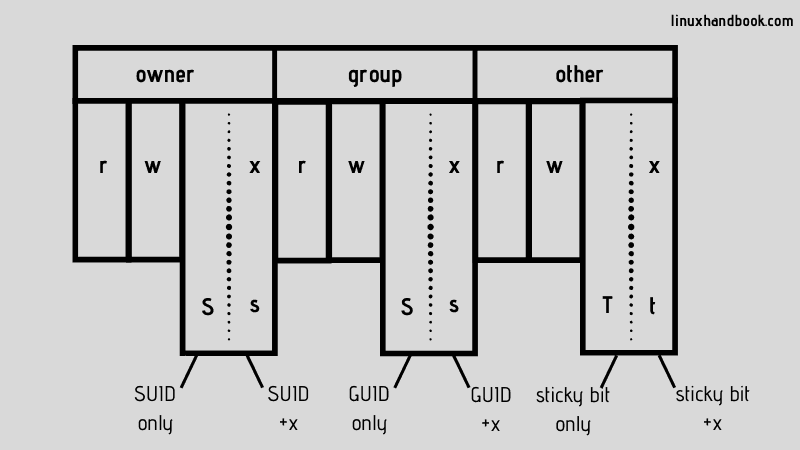
What Is Suid Guid And Sticky Bit In Linux How To Use Them

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions
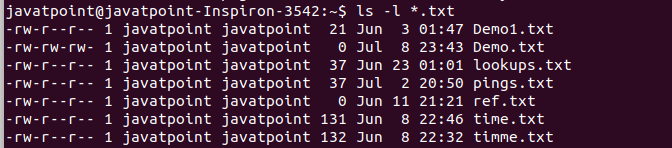
Linux Chmod Command Javatpoint
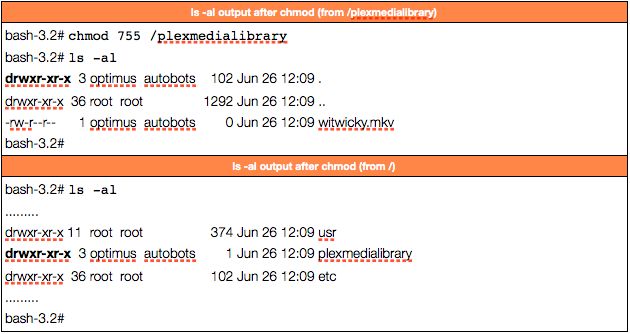
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
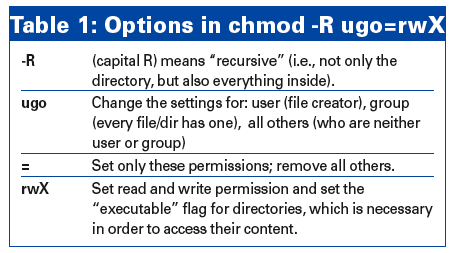
Ask Klaus Linux Magazine

File Security

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics
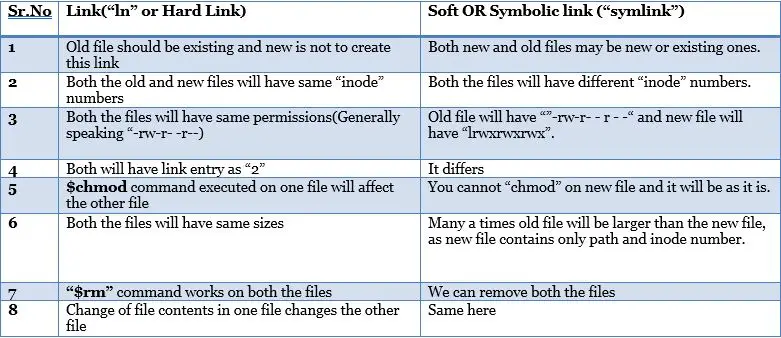
How To Create Hard And Soft Symlink Links On Linux Systems

Suse Linux Enterprise Desktop Administration Chapter 9 Manage Users Groups And Permissions Ppt Download

Basic Linux Commands

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsn38tloc9zbrrwdhcwtghkqo 2hlbiucmz1newmc5z3eczau8 Usqp Cau
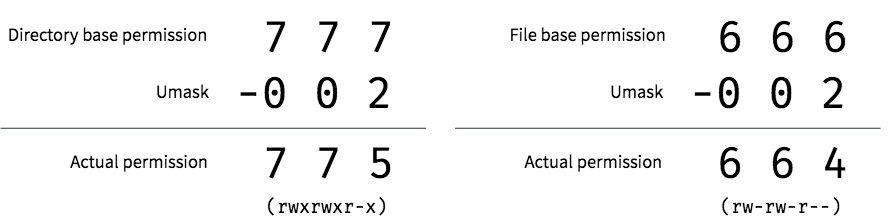
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux Training Academy




