Linux Chmod Directory And All Files
The chmod command only allows you to change the permission of files and directories that you own.

Linux chmod directory and all files. -name "rc.conf" -exec chmod o+r '{}' \;. Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory.
How to make a file writeable (chmod 777) Connect to your web server with your telnet software. Conclusion # The chmod command changes the file’s permissions. Normal files only (skip directories, symlinks, named pipes and sockets, and the special files found in /dev).
Files and directories in Unix may have three types of permissions:. Group — all users who are members of the same group. To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all).
Chmod command allows you to alter / Change access rights to files and directories. The root directory of the Linux is where the commands that -exec runs are executed. Sudo chmod -R 775 /var/www/example (this changed the permissions) after all of these done i am still able to use a user to create a file which is good as this user is in the group i created but the thing is that the permissions are all wrong and the file owner is also wrong.
The file or directory owner;. This option change files and directories permissions recursively. The “:group” is optional.
Change the permissions of the directory and all its contents to add write access for the user, and deny write access for everybody else:. You might consider using rw access for files and not enabling the executable bit. The following screenshot shows the execution of the command on a Linux Environment.
Chmod -R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree. Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command.
One of the easiest ways is to use the find command to select the files and then run the chmod command with the -exec switch. Yesterday I did something stupid which I today realised. Chown and chmod are the tools we use to manipulate ownership and access permissions of files and directories.
Also, both users and groups can be the owners of files and directories. There are several ways to apply a chmod to files recursively on Linux. $ chmod 777 file.
The options are r, w, and x. In Linux and Unix based systems access to all files and directories are controlled by file permission. Read (r), write (w), and execute (x).Each permission may be on or off for each of three categories of users:.
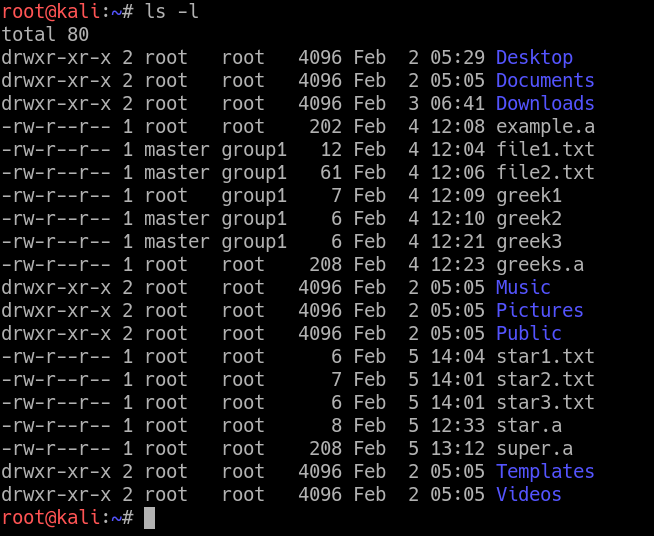
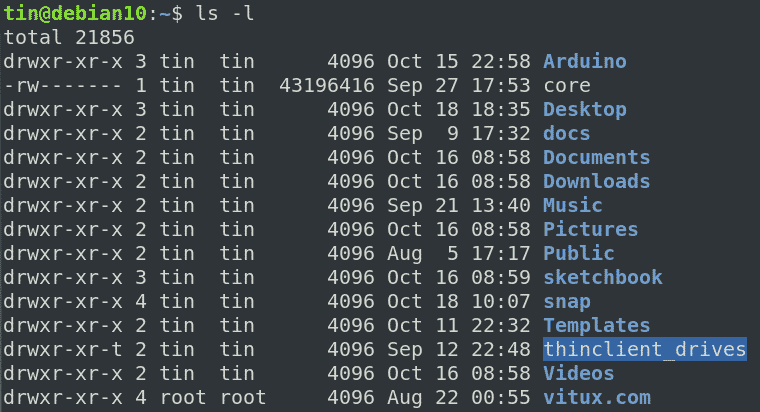
To change the mode of a file, use the chmod command. $ chmod -R u+w,go-w directory. Following is a sample of ls -l command output.
Chmod -R o+rwx <target directory> This command will give all users full access. Change into the directory with cd, before you run the find command. Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:.
Click below button to copy the code. In the example above, anybody belonging to the group can access the folder and see the files, but can't write to the folder. You can set the umask values in /etc/profile or in ~/.bashrc.
To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions. If they had 777 permissions Regardless of the permission (with ANY. Chmod Modifies File Permissions.
Chmod -R 755 directory chmod 777:. In a previous article, we looked at how to manage file & directory ownership using the chown command. Change the permissions of the file to read, write, and execute for all:.
Change directory with cd directory. Apply chmod 644 to all files only (excluding directory). $ find /home/user/demo -type f -print To find all files in /home/user/demo directory with permission 777, enter:.
How to change all file permissions to 644 and all folder permissions to 755 recursively using chmod in the following two situation:. As you might remember, the default file permission value is 0644, and the default directory’s is 0755. -type f -exec chmod 750 {} +.
Sudo chmod -R 755 Example. The file or directory owner;. To do this, use the uppercase -R flag:.
How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux. Linux - Solution 1:. In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users.
The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. $ sudo chmod <specify the file permissions> <specify the file/directory name>. $ find /home/user/demo -type f -perm 777 -print.
Hi, OS - Unix, linux (all unix flavors) My requirement. Ownership and Access Rights. To assign 755 permission of all files and directories under /opt/dir # chmod -c -R 755 /opt/dir.
In case you need to change the permission of files and directories that you don’t own, you will need to use sudo. How to chmod Files and Directories Recursively Written by Rahul, Updated on October 21, 15. Let's take a look at some other examples.
Iam trying to start with directory and here is my code in the file totalchange.sh (insideragain - is a directory, test1.txt - is a file under the directory insideragain) totalchange.sh file. Write – When write permission for a file is granted to user, he can modify contents of file. How to Set File Permissions Using `chmod' Files and directories in Unix may have three types of permissions:.
Chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions. In this tutorial, we will show you how to change file permissions recursively with chmod and find command in Linux. Permission is divided into three categories Read – This permission when granted allows user to open and read contents of files.
The permissions can be set using either the symbolic or numeric mode. How do I chmod a 777 file?. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions.
Enable the 'other' bits for the directories and files. You can also use chmod as the -exec option for find, which lets you change file permissions throughout the system. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode.
To check directory/file exists and then change the permission of the directories/files. The final characters are the permissions that all users have, and these are the same as the group permissions. Change permission on all the files in a directory recursively chmod has the recursive option that allows you to change the permissions on all the files in a directory and its sub-directories.
Use chmod to set additional file system modes for files and directories. It will not only apply the permission to the parent “files” directory but also to the files under it. However, if you need to apply conditional file permissions recursively, you need to use combination of the find and chmod command.
As well as details of ownership, each file has metadata about its access permissions. The find command will search for files and directories under /var/www/my_website and pass each found file and directory to the chmod command to set the permissions. In Linux / Unix systems, accessibility to files and directories is determined by file ownership and permissions.
Now, to verify if the permission is applied successfully, navigate to the “files” directory using the “cd” command and then run the “ls –l” command.From the following input, you can see that the permissions have applied successfully to all the files under the parent directory. The basic syntax of the chmod command is shown below:. This tutorial will explain you how to change different-2 permissions for files and directories recursively.
The default umask value is subtracted from the overall file/directory default value. Both chmod and chown can be run recursively on directories, to change file permissions for everything within those directories. Removes all privileges for all:.
Chmod -R rwxrwxrwx path-of-the-directory. To find all files in /home/user/demo directory, enter:. How to Change File and Folder Permissions.
There are three sets of permissions. Chmod is command line utility for changing permissions of files and directories under Linux/Unix operating system. The hyphen means that a permission is missing.
The format of the command is chmod XXX -R directory-location. Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions on files and directories. /root# chmod o-rwx * .* This supposed to remove read, write and execute permissions for the world on all files in the current directory (/root).As soon as I did this, screen behaved weird, I couldn't run commands as a non-root user, and ssh refused to work unless I logged in with root.
To change all the directories to 755 (drwxr-xr-x):. Find ./mydir -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;. Chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems.chmod stands for change mode.Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory.
For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:. This would also remove any special permission if already assigned to any of the files or directories under /opt/dir. In this tutorial, we look at the chmod.
Chmod -R permission directory Therefore, to set the 755 permission for all files in the Example directory, you would type:. For example, give full access to the directory permission recursively with all sub-directories and files:. Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone.
The command gives read, write, and execute privileges to the owner ( 7) and read and execute access to everyone else ( 55 ). Type chmod 777 * to change mode for all files in that directory. For example, I created a file with Sticky Bit Special permission under /opt/dir.
Chmod 700 -R directory. Chmod -R 777 permissions. The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory.
To learn more about chmod visit the chmod man page. If you only want to change mode for a special type of file your can use chmod 777 *.txt *.dat orchmod 777 filename.ext. By - Linux tutorial - team.
Let's look at the command for gzip, a file compression utility for Linux. The basic syntax is:. To make this possible you can use the find command and search for all files with a .sh extension and then run the chmod command on each one found:.
Apply chmod 755 to directory and sub-directories only (excluding files). This filters all objects in the current directory tree (.) for files named rc.conf and runs the chmod o+r command to alter file permissions of the results that find returns. Other people in the same group as the owner;.
You can set the sticky bit permission to file1 with the following command:. The command executed here is chmod 777 -R home and it gives 777 permission to the folder home itself, also to all of the files and sub-directories inside this folder. Using symbols (alphanumerical characters) using the octal notation method.
Read (`r'), write (`w'), and execute (`x'). Each permission may be `on' or `off' for each of three categories of users:. In Linux, users can belong to one or more groups.
$ chmod u=rw,go= file. File Permission is given for users,group and others as,. Find /directory/of/interest/ -type f -iname "*.sh" -exec chmod +x {} \;.
We will be using the chmod command to change file and folder permissions in Linux. 4= set permissions of this directory to 775 -- used command:. Cd /var/www/mydirectory find.
To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option. You can also set the sticky bit permission to file so that only the file owner the root user can delete the file. Other people in the same group as the owner;.
Im a newbie with this Linux stuff but our Novell webserver crashed (hard drive) and thought to put Novells version (SUSE 10.0) instead. We have the root folder for our website at /etc/apache2/htdocs We chmodded that folder and all sub-directories with all the commands that you posted on here and seemed to work. Here we have the commands that anybody can use on the Linux system.
Basic Syntax of CHMOD Recursive. Owner — the user who creates and owns a file or folder. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else.
Find /opt/lampp/htdocs -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;. But first, you need to be aware that there are three types of users who can interact with a file:. An interesting place to look at different kinds of file permissions is the /bin directory.
Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits. You can use the find command. Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY.

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
Linux Chmod Directory And All Files のギャラリー

Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory
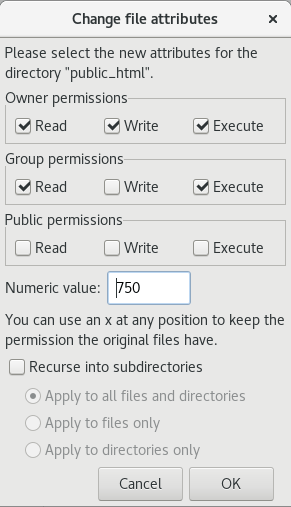
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support
Change Permissions Of Files And Folders In Filezilla In Your Linux Hosting
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsuqrd7yr237u Am8msiqf70j96klzxefjagdqqwjyc32uhwnrw Usqp Cau

Directories Showing Up In Green Executable Even After Removing Execute Permission For All Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Linux Users And Groups Linode

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Linux Users Permissions And Management Programmer Sought

How To Copy Files Using The Install Command On Linux

Solved B To Remove Myfile Ordinary File From The Paren Chegg Com
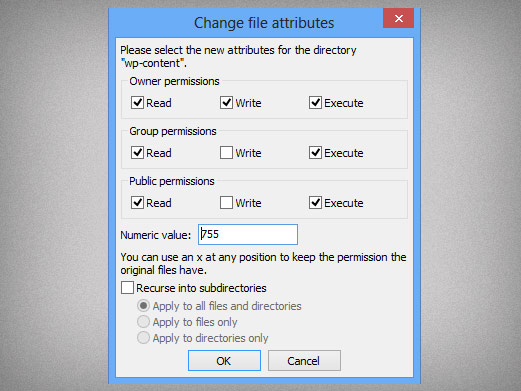
What Is Chmod How To Use Chmod For Wordpress File Permissions

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu
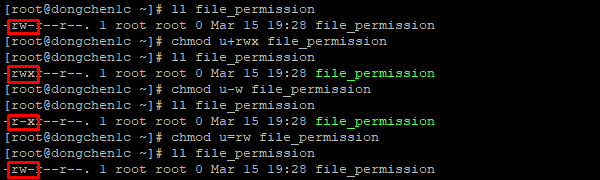
44 File Permissions Chown Chgrp Chmod Umask Dong A Place To Track My Time Log

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Write Access Chmod 644
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Give Write Access Chmod Command
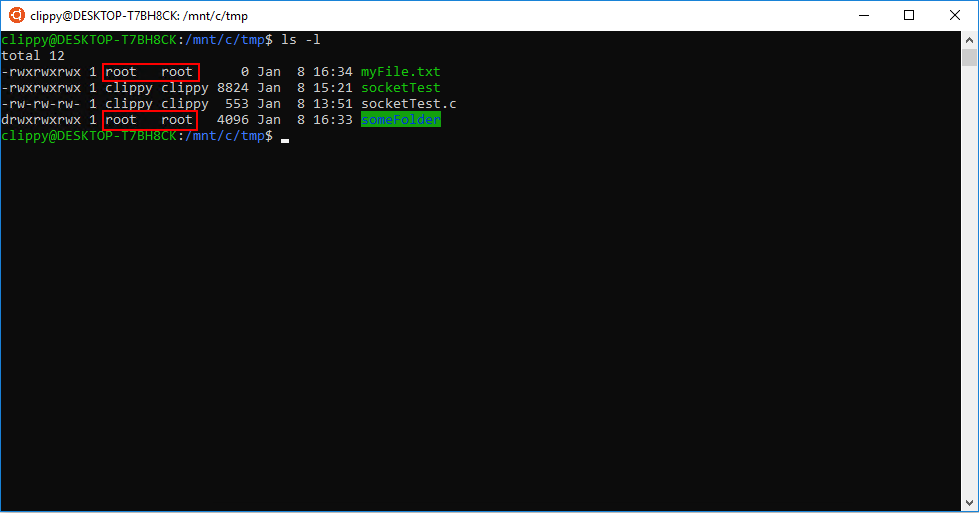
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Understanding File Permissions

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

14 Permission And Modification Times
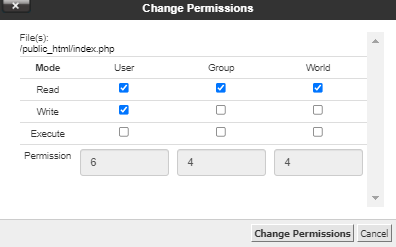
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

How To Chown Recursively On Linux Devconnected

Linux File Permission Change By Chmod Command In Linux Guide For Beginners

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
How To Create A Read Only File In Your Home Directory In Unix Quora

How To Change Permissions Folder And All Its Subfolders And Files In Linux

How To Use The Linux Chown Command Tutorials
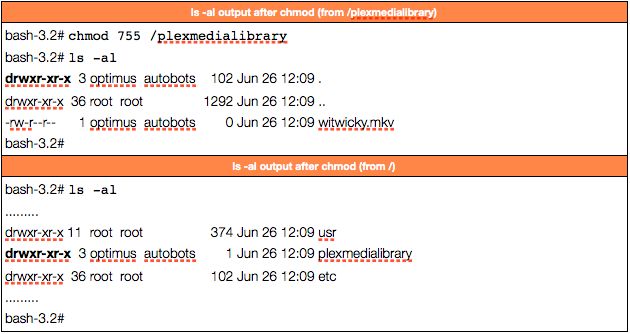
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org
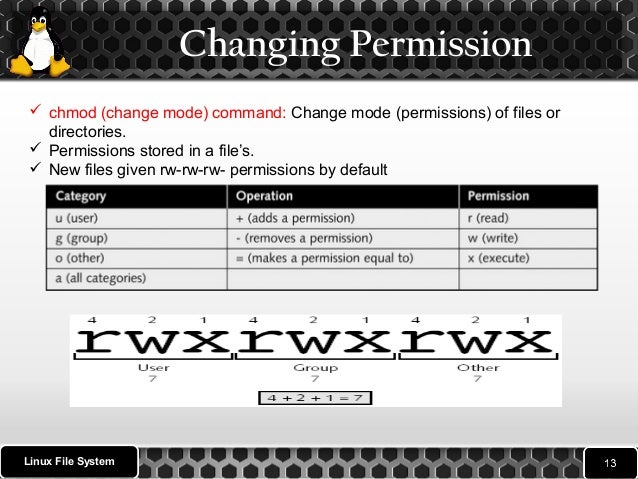
Chmod Change Mode Permissions
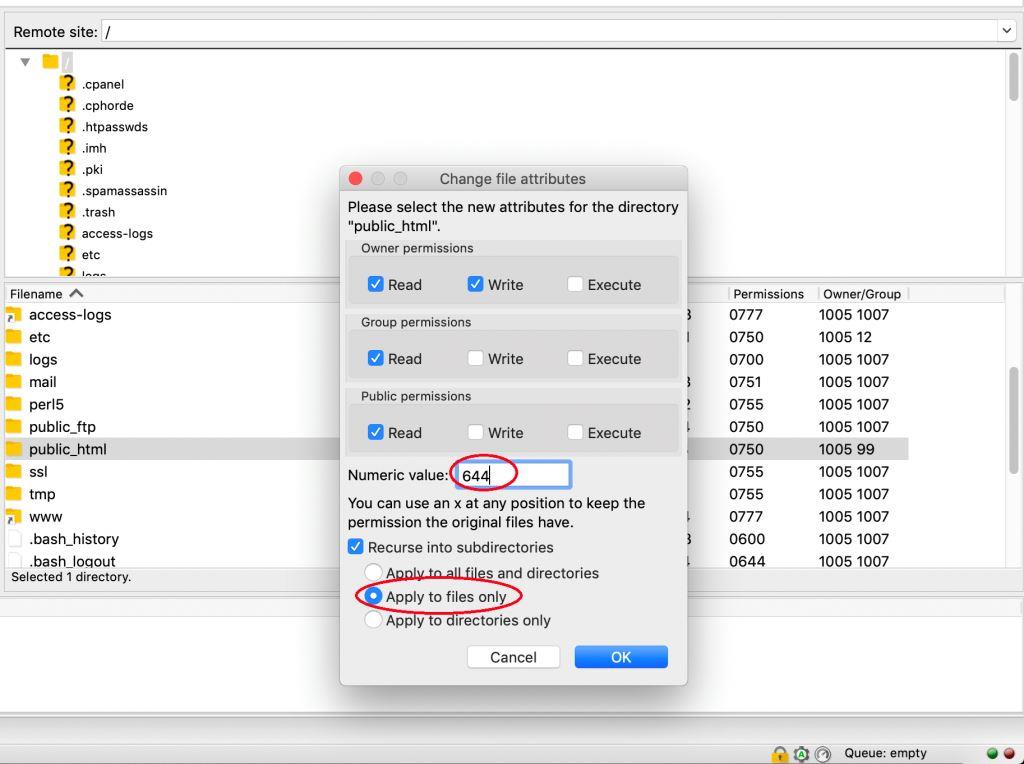
How To Assign The Correct Permissions To My Prestashop Files And Folders Rolige

Xampp Htdocs Permission Issue And Fix In Ubuntu

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Linux Jessica Peng

Solved Users Permissions 1 Review The Adduser And Chmo Chegg Com

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Quick Answer How To Use Chmod In Linux Os Today

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
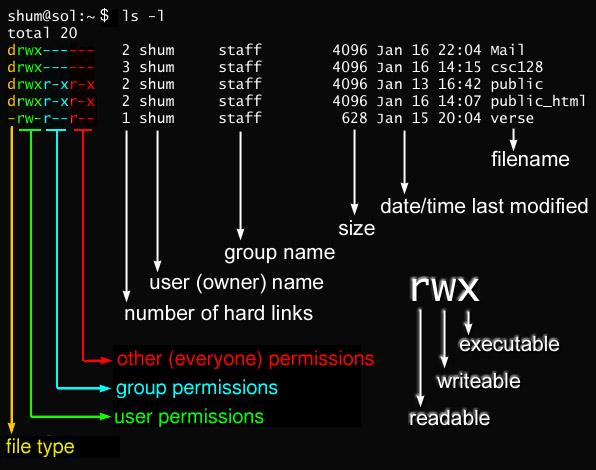
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Command Line Change Folder Permissions And Ownership Ask Ubuntu

Chmod Wikipedia

File Permissions In Linux Programmer Sought

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint
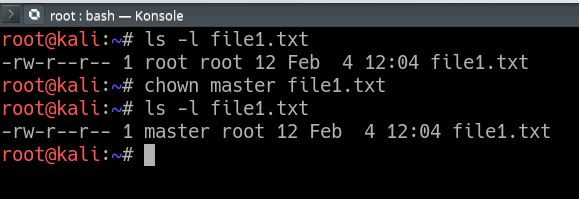
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gct I9jvgnhaxowmpzpaajfkfizchmnvqt Bi Nz3ljrxwqpkb8l Usqp Cau

Lesson 9 Setting And Using Permissions Overview Describing File Permissions Using Execute Permissions With A File Changing File Permissions Using Mnemonics Ppt Download

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
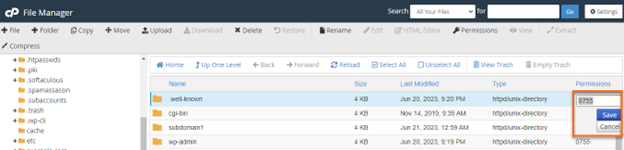
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

How To Use Chown Command For Beginners Lintut
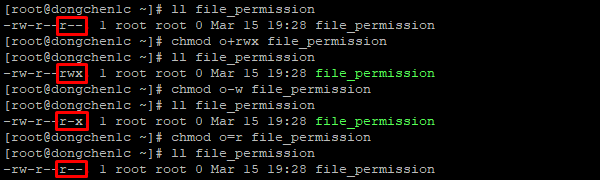
44 File Permissions Chown Chgrp Chmod Umask Dong A Place To Track My Time Log
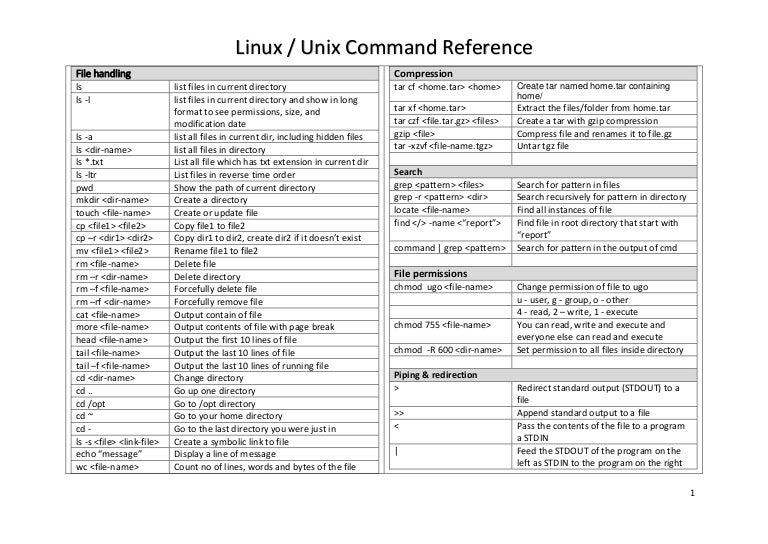
Unix Linux Command Reference
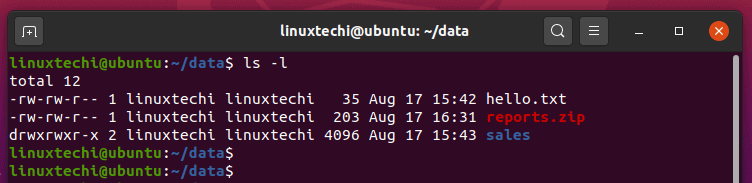
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Unix File Permissions Computer Science

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
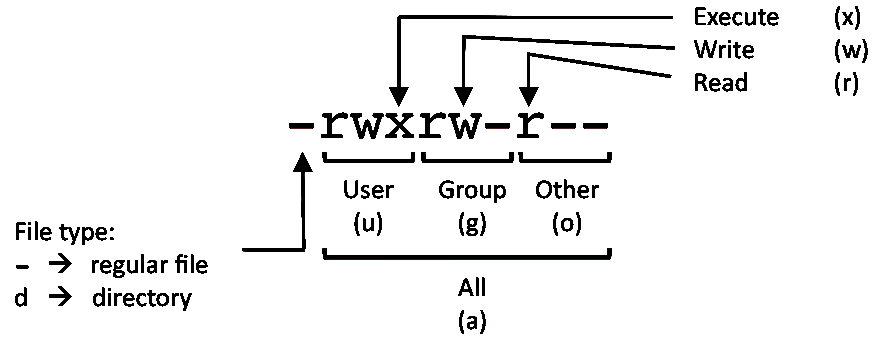
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux Training Academy

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize
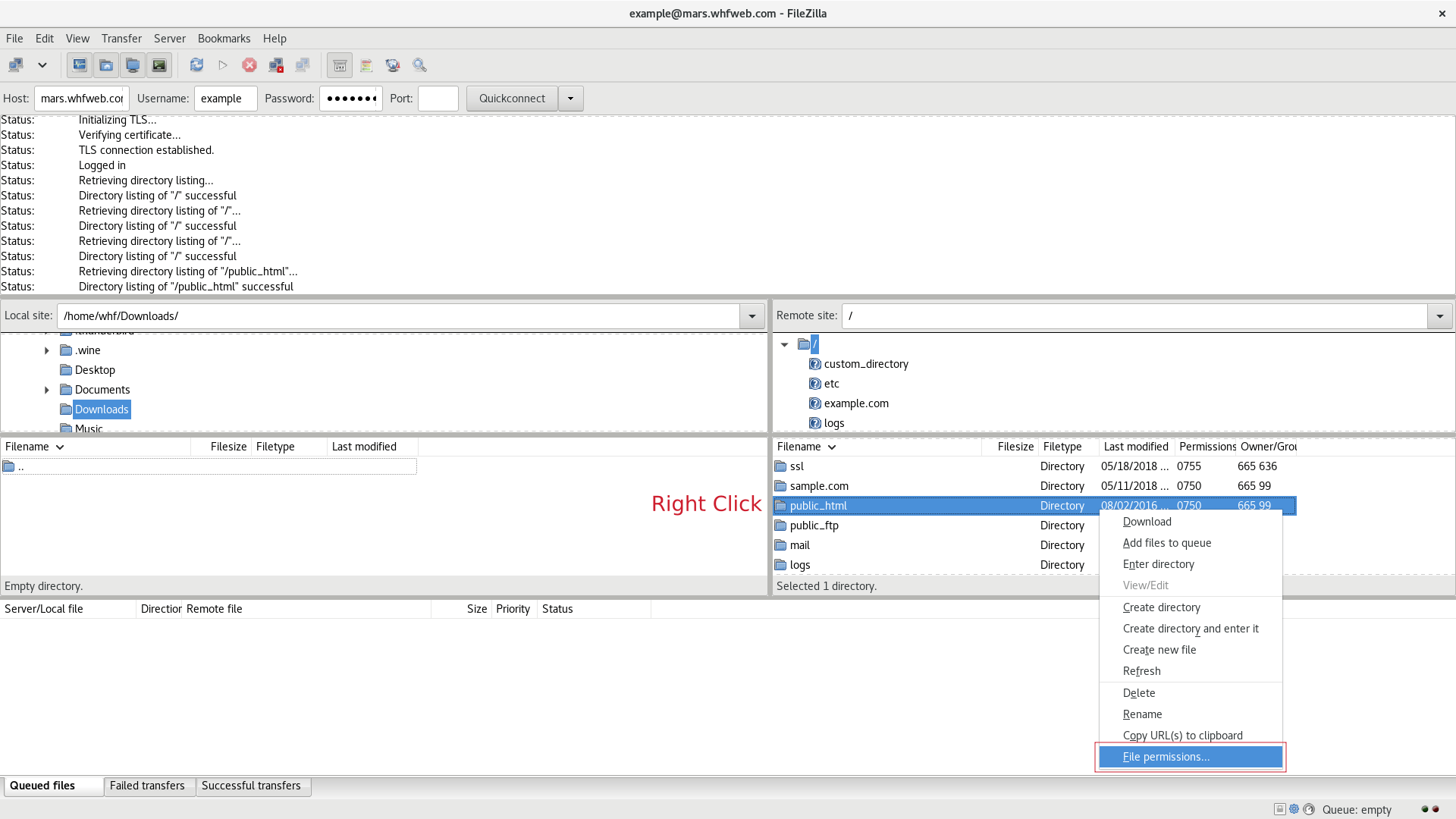
Change Permissions Of Files And Folders In Filezilla In Your Linux Hosting
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
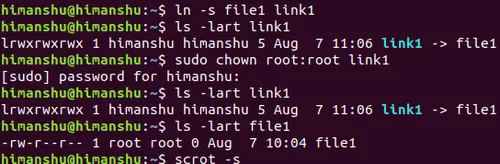
Linux Chown Command Tutorial For Beginners 12 Examples

A Complete Guide To Chmod Recursive Force And More

Understanding File Permissions And Access Rights In Linux Linux Stall

Agenda The Linux File System Chapter 4 In Text Ppt Download
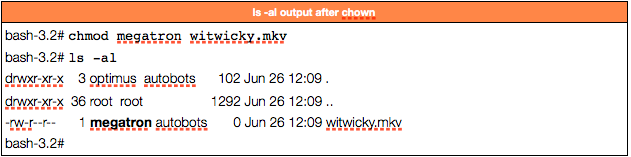
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu

Linux It S Me Tommy
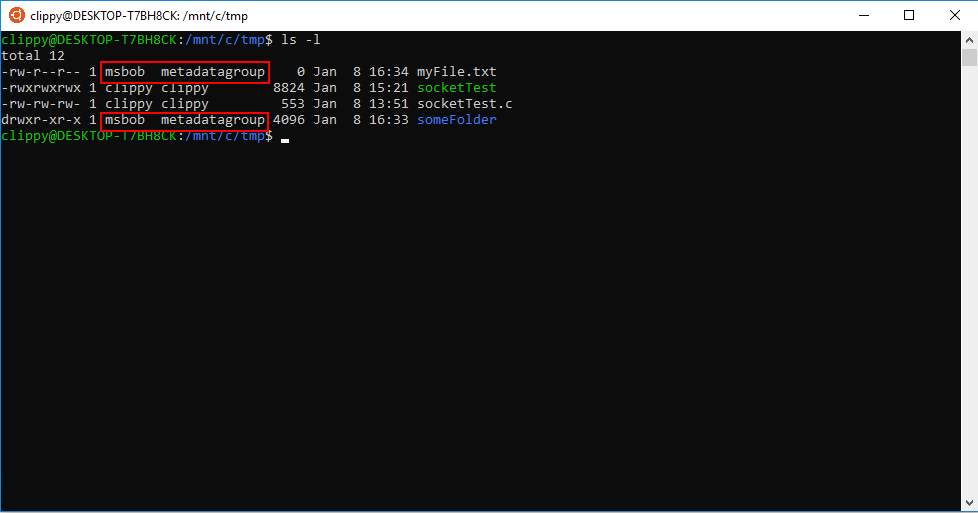
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line
2




