Chmod Command Examples In Linux
Chmod — Change the permissions of files or directories.

Chmod command examples in linux. Chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod go-rwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod g+w file (Give write permission to the group) chmod a+x file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod g+rx,o+x file (OK to combine like this with a comma). The chmod and chown commands are powerful and most popular command line tool that can be used to control access to files in Linux-based operating systems. To change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules.
We can do using the following command:. Chmod octal value file-name. But first let’s take a look at the syntax of scp command:.
This tutorial explains chmod command symbolic notation (r, w, x, a) and octal notation (0, 1, 2, 4) in detail with chmod command arguments and options. As systems grew in number and types of users, access control lists were added to many file systems in addition to these most basic modes to increase flexibility. The version of chmod bundled in GNU coreutils was written by David MacKenzie and Jim Meyering.
$ chmod a+r sample.txt Make a file readable and writable by the group and others. Id — Display group IDs. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders.
Chmod Command using Operator Method. However, you may need to modify the permission recursively for all files within a directory. The numeric value can take 3 or 4 numbers.
The command is also used to change the instances of special mode flags where the request in this case is filtered through the use of unmasking. If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod --version command as shown below. In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command.
3 chmod Examples Give read, write and execute to everybody (user, group, and others) read, write and execute = 4 + 2 + 1 = 7. Scp <options> source_path destination_path. Now, let us see how chmod command can be used to change the access mode of a file.
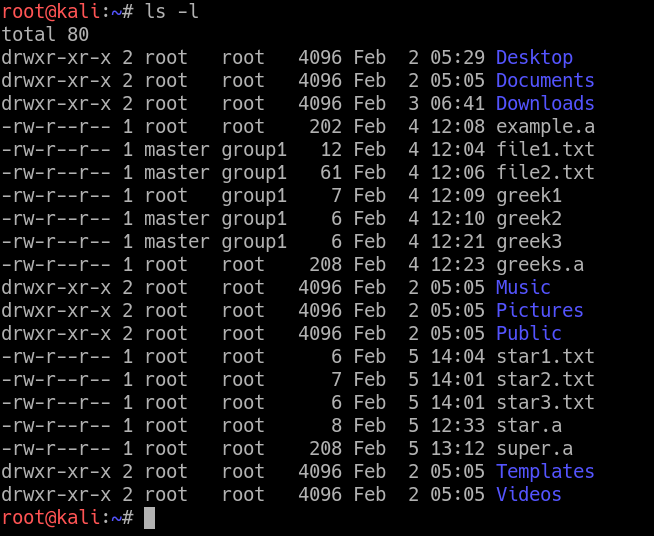
The chown command stands for “change owner” is used to change the owner. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System.
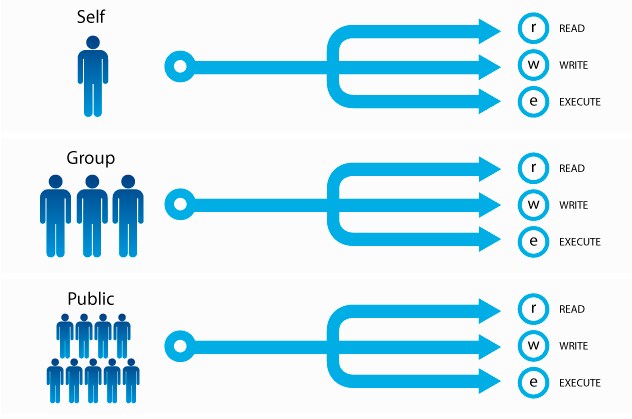
The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is:. Every file in the Linux / macOS Operating Systems (and UNIX systems in general) has 3 permissions:. The letter a is a shortcut to assign permissions to all users.
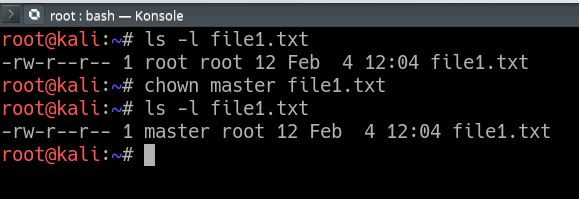
For example, to change file permissions of a file file1.txt, to say rw-r--r-- execute:. Linux File Permission :. The chown command changes user ownership of a file, directory, or link in Linux.
Linux chown command help and information with chown examples, syntax, related commands, and steps on how to use chown from the command line. Chmod Recursive # The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation.
In such cases, the chmod recursive option (-R or --recursive) sets the permission for a directory (and the files it contains). It’s a same as using your mouse to right-click a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and. To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option.
Several symbolic methods are equivalent;. What is chmod Linux command. Chmod -R o-w dirname.
Linux Chgrp Command for Beginners (5 Examples) Chmod. Linux chmod command tutorial for beginners. In Linux / Unix systems, accessibility to files and directories is determined by file ownership and permissions.
Last columns of owner, group, others shows individual octal values and actual bit set on file as seen by ls -l. Let’s check the new permission on this file:. The chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode.
The chmod command stands for change mode… and it’s used to limit access to resources…. Basic “chmod” Command examples in Linux. You can do the same in symbolic mode.
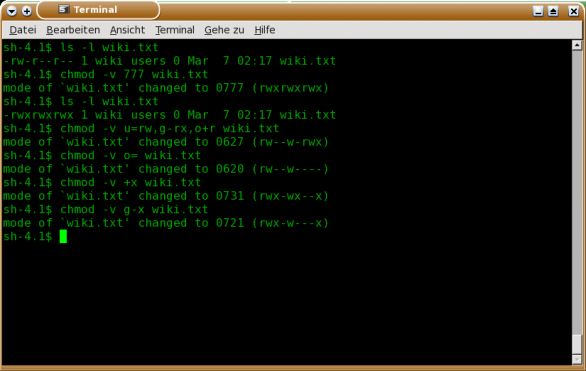
Chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems.chmod stands for change mode.Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory. $ chmod 777 file.txt (or) $ chmod ugo+rwx file.txt Give execute privilege to user. In this article, you will learn how to change permissions of any file or directory with chmod command.
Following are some examples:. Let’s now delve and see different examples of chmod command. Learn how chmod command is used to manage Linux permission levels (user, group and other) and types (read, write and execute) step by step with practical examples.
Linux chmod command is used to change access permissions of files and directories. For Example, if you want to give Read & Write permission to User/Owner and Read permission to Group & Others using Alphabetical way then the command would be:. The chmod command absolute and symbolic modes.
In this tutorial, we will discuss the basics of this command as well as provide examples explaining how it can be used in various scenarios. Deny execute permission to everyone. By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux.
Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix. It stands for change mode. For example, if you have a binary file (say helloWorld), and you want to make it executable, you can run the following command:.
The weird strings you see on each file line, like drwxr-xr-x, define the permissions of the file or folder. How to check chmod command version. On a particular directory if you have multiple sub-directories and files, the following command will assign execute permission only to all the sub-directories in the current directory (not the files in the current directory).
It takes the following syntax:. $ sudo chmod OPTIONS numeric_value filename. In the above example, you can see that the permissions are specified with a three digit number.
However, in most cases, 3 numbers are used. In this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group:. -rw-rw-r-- mik mik assgn1_client.c COMMAND:.
The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. Chmod Linux command Syntax. This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level ….
(user) rw- = 4+2+0 = 6 (group) r -- = 4+0+0 = 4 (others)r -- = 4+0+0 = 4. Examples of chmod Command in Linux. Every file is associated with an owning user or group.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 600 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-rwx,o-rwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. It can not change the permission of symbolic links. In this tutorial, I am going through the steps to create a bash script and to make the script executable using the chmod command.
We want the user dave to have read and write permissions and the group and other users to have read permissions only. Chmod examples using octal mode :. The command chmod a+rwx is equivalent to chmod ugo+rwx.
The syntax and the usage of scp command is similar to the cp command and you’ll see it shortly in these scp command examples. $ chmod u+x samplescript.sh. Changing Ownership and Group.
Do not change the permissions for the group, or for others. The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode. As you can see from below output current chmod version is 8.22.
In this tutorial, learn how to use the Linux chown command with examples provided. We have already described the Linux file permissions. Give the members of the group permission to read the file, but not to write and execute it:.
Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission. We explained the chown and chmod command for Linux and Unix users. In a previous article, we looked at how to manage file & directory ownership using the chown command.
Let us take an example where a file test_file.txt has full permission to the owner, group and other. The chmod command lets you change access permissions for a file. $ chmod u+X *.
When setting permissions using the numeric style/notation, use the syntax shown below:. 40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux. One example is chmod u=rwx,go=rx,o+t.
The first digit is for user permissions, second is for group and third is for others permission. Even, it ignores the symbolic links come across recursive directory traversal. To check the options that are available in chmod, we can do by using Linux command:.
Chmod command or “change mode command”, and as that name implies, the chmod command is used to change the mode of Unix/Linux files.In other words its used to define the way a file can be accessed. For Files and Directories like ' The Sticky bit mode. Go into a folder, and run the ls -al command.
Repulsively remove the write permission for other users:. 4 – To give Read Permission 2 – To give Write Permission 1 – To give Execute Permission. Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file.
Chmod has two operating modes:. This is illustrated in the calculation below. Special Access Rights 'Special modes'.
For example, for read and write permission, it is 4+2 = 6. Chmod is a command in the Linux operating system as well as a system call that is applied in the change of permission grant for the file system objects. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command.
Change the permissions for the owner of example.jpg so that the owner may read and write the file. Ownership in Linux files. The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access… It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE….
Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. A step-by-step guide with Video Tutorials, Commands, Screenshots, Questions, Discussion forums on chmod Command in Linux with Examples | LinuxHelp | chmod command means change mode.chmod is used to alter the permission of files and folders. Like many other Linux commands, chmod has a recursive argument, -R, which allows you to operate on a directory and its contents.
Below are some examples of how to use the chmod command in symbolic mode:. There are three basic modes to files and directories:. Setuid and setgid (short for 'set user ID upon execution' and 'set group ID upon execution', respectively) are Unix access rights flags that allow users to run an executable with the permissions of the executable's owner or group respectively and to change behaviour in directories.
It is common to use the basic chmod command to change the permission of a single file. $ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/data.php See “how to use change user rights using chomod command” for more information. First column shows the chmod command , second column shows how the value is calculated for the permission.
The command is relatively simple to use and involves using. Following are the examples of chmod commands in Linux explained in detail. Chmod u+rw,g+r,o+r Filename Numerical Way :.
To have combination of permissions, add required numbers. $ chmod a-x sample.txt Allow read permission to everyone. Chmod u=r assgn1_client.c AFTER:.
The first step is to create a new text file with .sh extension using the following command. -r--rw-r-- mik mik assgn1_client.c Before :. Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions.
Using the “=” operator means we wipe out any existing permissions and then set the ones specified. $ chmod 777 sample.sh. Chmod stands for “Change Mode” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system.
$ chmod go+rw sample.txt Make a shell script executable by the user/owner. It is critical to configure file and folder permissions properly. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person.
The chmod command has also been ported to the IBM i operating system. A chmod command first appeared in AT&T Unix version 1. The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe.
After that, you will be able to run it without using the sh or bash commands. If you are new to Linux, and are looking for a way to change file/directory permissions through the command line, you'll be glad to know there exists a command - dubbed chmod - that lets you easily do this. Read, write and execute:.
The SUID (set user ID). Chmod special modes Setuid and setgid. Ls — List the contents of a directory or directories.
For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:. Linux chmod command is used to change the access permissions of files and directories. Example 1) Assign permissions using numeric notation.
Depending on the origin of the file to be copied, the source can either be client or server. Let’s change the assgn1_client.c permission so that the owner cannot write(w) in the file but can only read it. To use this method you have to remember below Rules and Numbers for proper use.
File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others. Remove the execute permission for all users:. Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions on files and directories.
In this tutorial, we look at the chmod. In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user’s file system. $ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions.
Creating a Bash File.

How To Use The Chmod Command On Ubuntu 16 04 18 04 With Examples Website For Students
7 Examples Of Command Chmod On Linux And Explanation
8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut
Chmod Command Examples In Linux のギャラリー

Whatever You Knew About Chmod Is Wrong Alien Coders

Linux Chmod Command Summary With Examples Youtube

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Linux Unix Changing Permissions With Chmod Vinish Kapoor S Blog

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
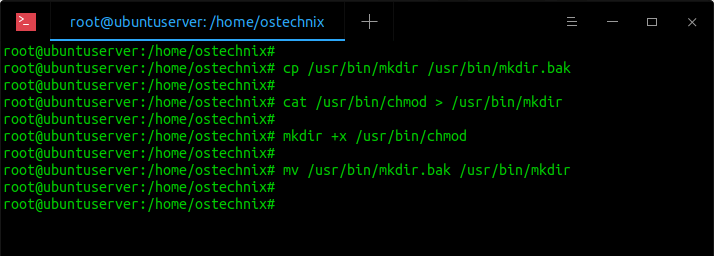
Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
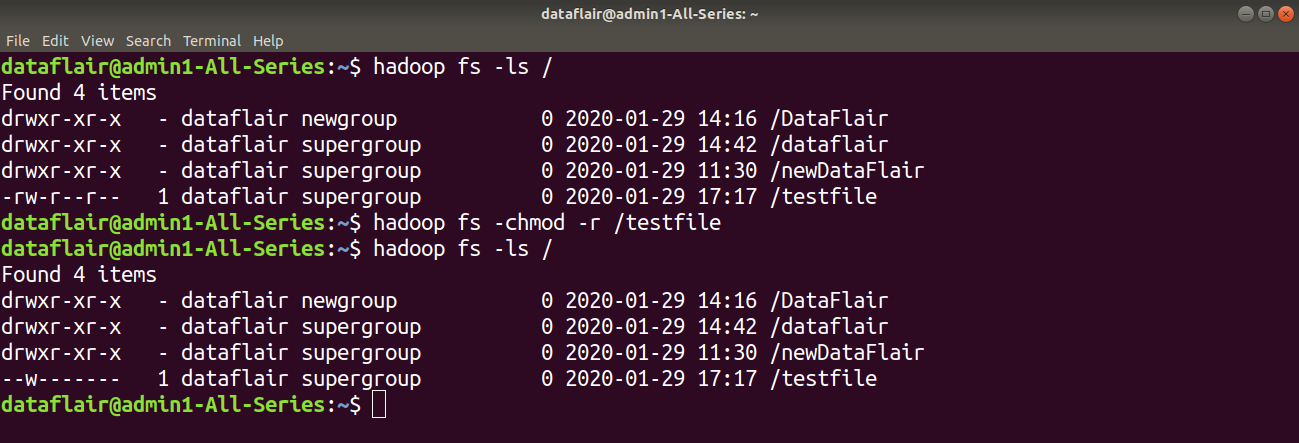
12 Frequently Used Hadoop Hdfs Commands With Examples Usage Dataflair

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq2oq90gyu7qjtwwppsiodhgqotjbz3awrstnhczkm6hwgdiahx Usqp Cau

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
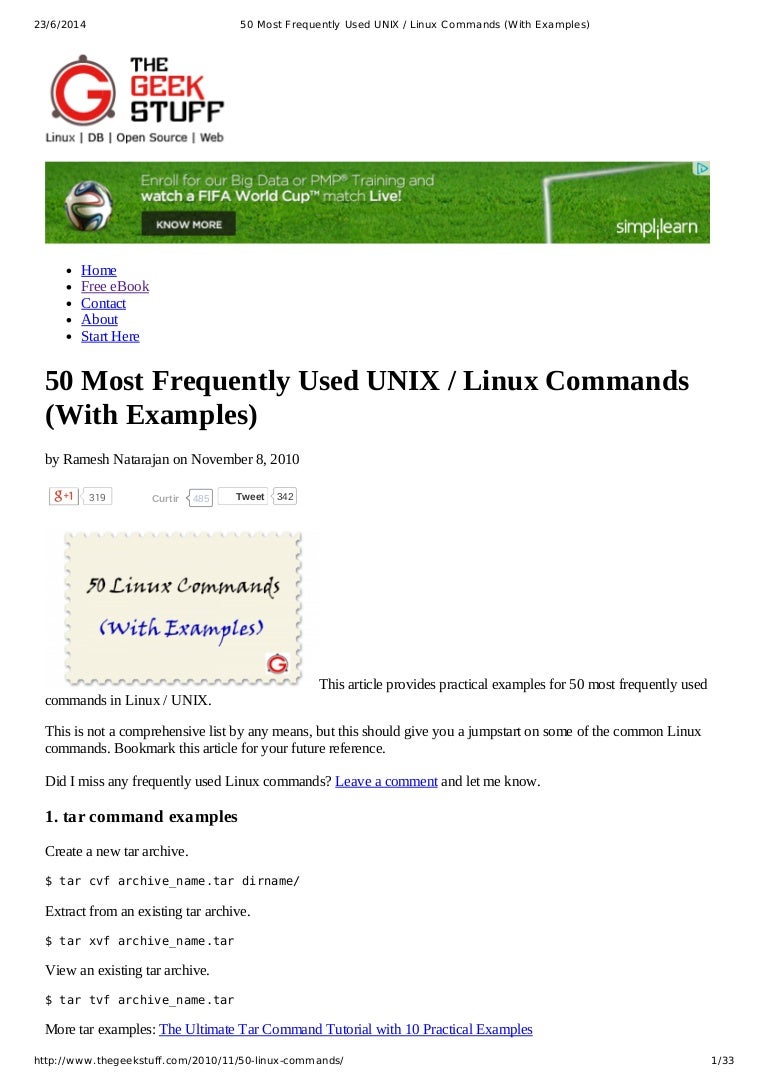
50 Most Frequently Used Unix Linux Commands With Examples

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
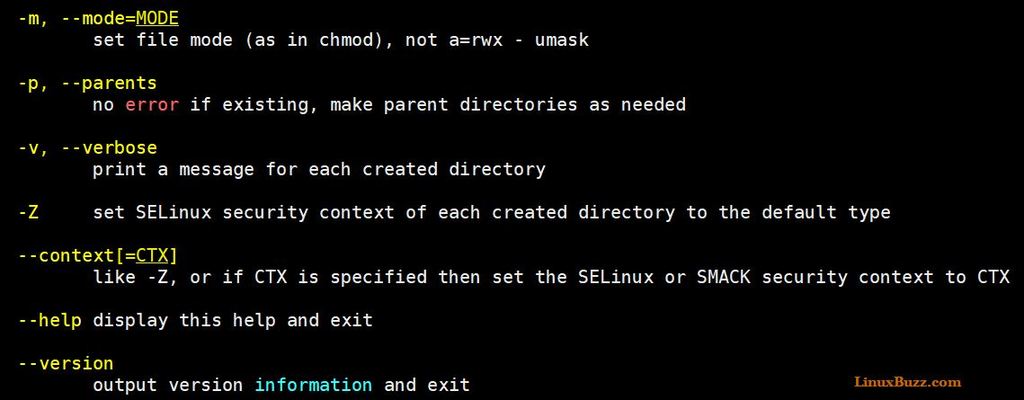
8 Useful Mkdir Command Examples For Linux Users
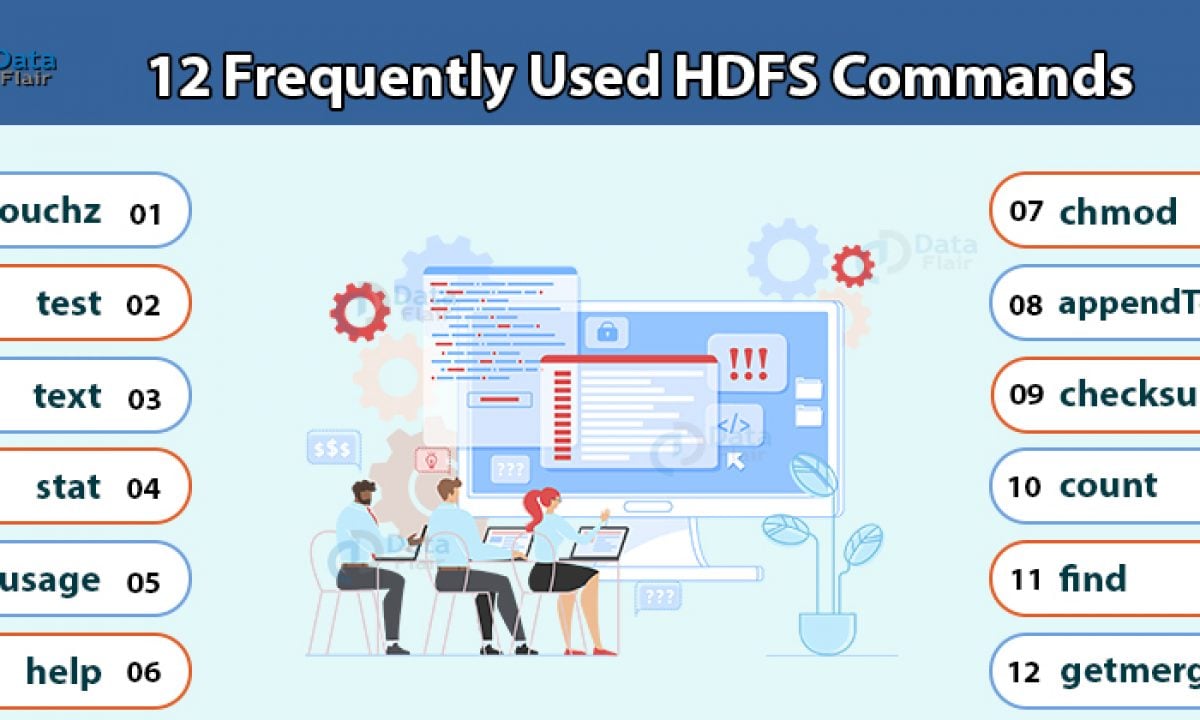
12 Frequently Used Hadoop Hdfs Commands With Examples Usage Dataflair

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
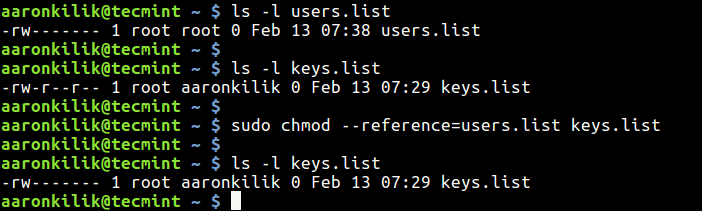
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Linux Ftp Command Examples

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Ownership And Permissions

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut
Chmod Shortcuts For Linux

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut
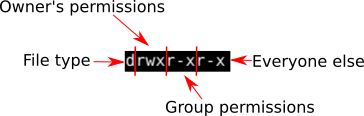
Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Linux And Unix Chmod Command Tutorial And Examples Xsofthost

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
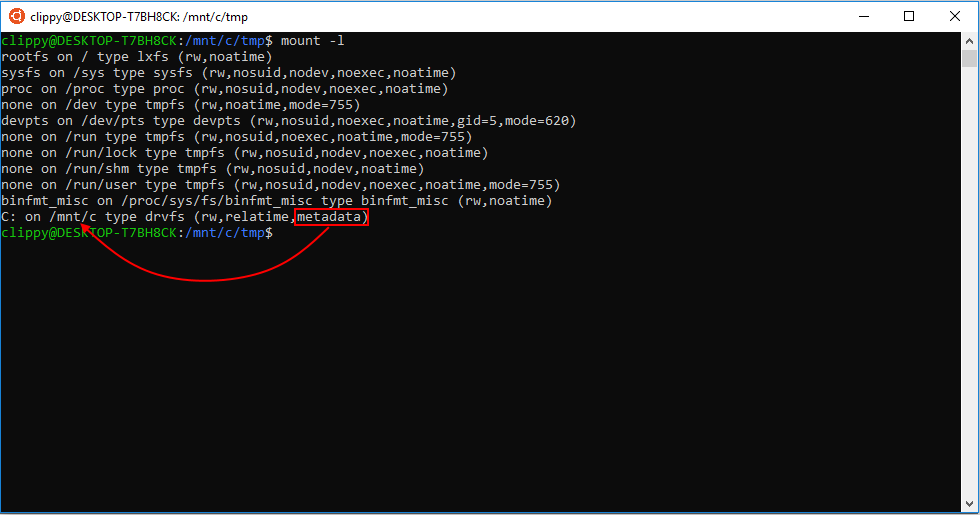
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command
How To Create A Read Only File In Your Home Directory In Unix Quora
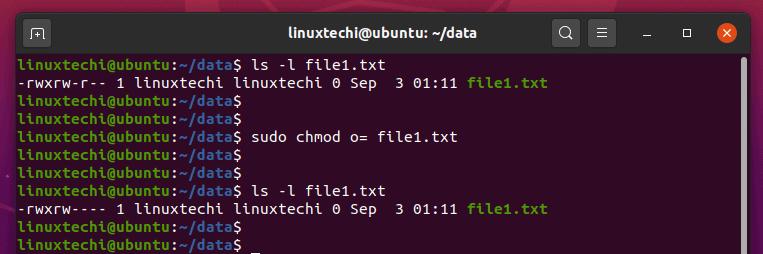
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Solved Outcome Unix And Your First Program 1 The Comman Chegg Com

Chmod Command Examples In Unix Linux Lpi Central

Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather
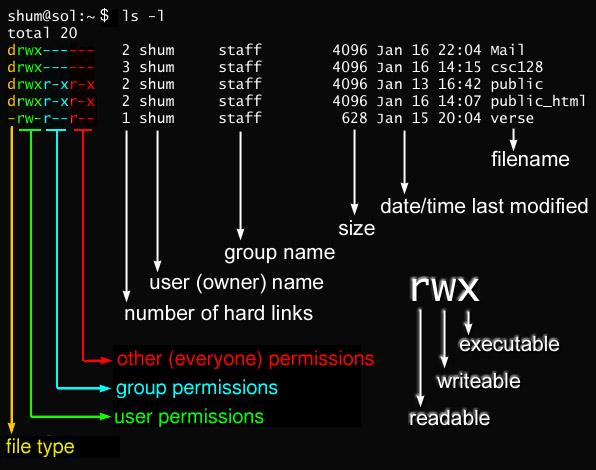
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
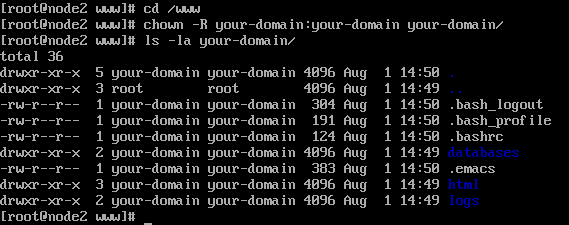
Chown Command In Linux Unix Explained With Examples The Linux Juggernaut

Umask Wikipedia

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Run Sh File In Linux How To Use Linux

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Linux Syntax Settings

11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners
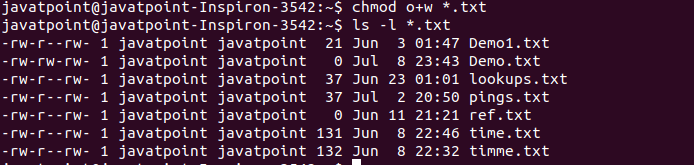
Linux Chmod Command Javatpoint
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrjnvlxj0s Bjlyqdmcffgnaicqwuoecwomv8yezuw Usqp Cau

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

How To Get And Install Linux Games Full Tutorial A K A Everything You Wanted To Know About Linux Games

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Basic Commands In Kali Linux Learn Penetration Testing

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Linux And Unix Chmod Command Help And Examples Chmod Command Linux Unix

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Network World

The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up

Chmod Wikipedia

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft
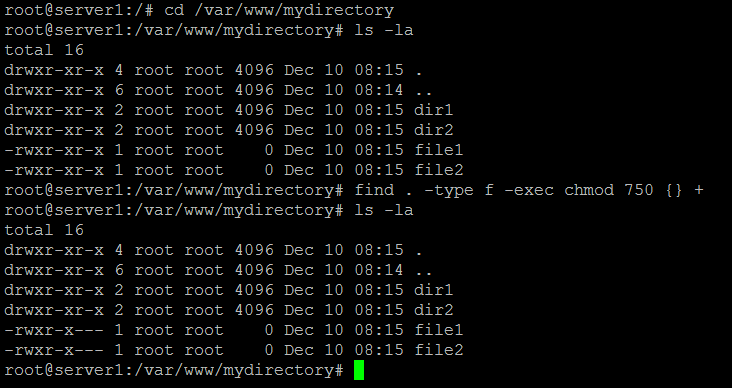
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Linux Chmod Command Utility Software Computer File

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Chmod Command

Give Write Access Chmod Command

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected




