Linux Chmod Directory And Contents
Table of Contents Sooner or later in the Linux world, you will have to change the permission on a file or directory.

Linux chmod directory and contents. It will not only apply the permission to the parent “files” directory but also to the files under it. In this article, I’ll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command. Unix & Linux Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for users of Linux, FreeBSD and other Un*x-like operating systems.
If we only want to change permission of directory we need to specify the type as directory. $ chmod -R 664 /opt/lamp Change Directory Permission with Find. Examples chmod 644 file.htm.
Run a file/script as command:. Permission is divided into three categories Read – This permission when granted allows user to open and read contents of files. Chown -R 755.
By joining our community you will have the ability to post topics, receive our newsletter, use the advanced search, subscribe to threads and access many other special features. Users can read file. The basic syntax of the chmod command is shown below:.
If you use the -R switch (like chmod -R) on a directory, it'll affect everything in that directory. Linux - General This Linux. For a directory, whoever has `read' permission can list files using the ls command (and thus discover what files are there);.
But generally its not a good practice to give 777 to all files and dirs as it can lead to data insecurity. Chmod a+X * This is very handy to make a whole directory tree readable by anyone, but not setting the executable bit on any regular files:. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions.
One of the most popular options that you can combine with chmod and chown is -R (Recursive). Chmod -R a+rX *. The basic syntax is:.
Alot of them are nested, so I can't just chmod the directory and then set the files back to what they were before. Replace directory with the directory path that holds the files and subdirectories you want to configure. Chmod Recursive # The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode.
Chmod is an abbreviation for change mode;. We can specify the type as file and change only files permissions. Chris Down’s answer could still fail if there are a lot of files in the first directory.
Group can read only;. To learn more about Linux file and directory permissions, search on the Web or use the Linux man command to research the chmod and umask commands. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command.
Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;. The chmod command in Linux/Unix is abbreviated as CHange MODe. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command.
The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. The -type x option searches for specific type of file only, where d is used for finding directory, f for file and l for link. Chmod -R 755 myfiles.
In Linux and Unix based systems access to all files and directories are controlled by file permission. $ find /opt/lamp -type d -exec chmod 660 {} \;. It is a useful tool which allows changing file system permissions using a terminal session or a terminal emulator.
Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write. This is done with the chmod command. Let us understand the Permission system on Linux.
It has -R or –recursive option that change files and directories. Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:.
Note that the group must exit before you can assign groups to files and directories. This option change files and directories permissions recursively. Chmod command is useful to change permission for Files and folders in Linux/Unix.
Users can update, write and delete a file from the directory. Write – When write permission for a file is granted to user, he can modify contents of file. Apply chmod 644 to all files only (excluding directory).
Is there an easy way out to achieve this on a Linux or Unix-like systems?. Chmod -R rwxrwxrwx path-of-the-directory. The Linux command chmod allows you to control exactly who is able to read, edit, or run your files.
To find out the mode of a directory:. Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:. You are currently viewing LQ as a guest.
By issuing these commands, you can change groups of files and directories in Linux. Users can execute/run file as command and they. Others can read only".
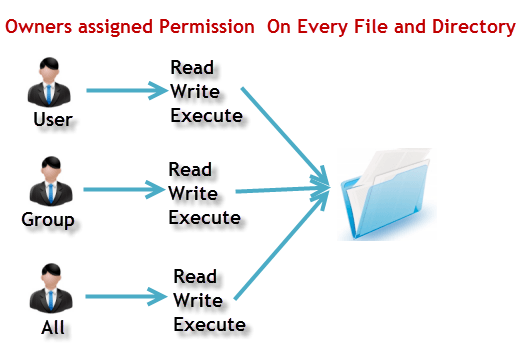
You can set the umask values in /etc/profile or in ~/.bashrc. The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory. Every file and directory in your UNIX/Linux system has following 3 permissions defined for all the 3 owners discussed above.
To selectively change permission, use find command to get the directories or files and then change mode. Applying the chmod and chown commands dynamically to the output of find command. This Linux option allows you to change permissions or owners of all files and subdirectories inside a specific directory.
If you want to use an option, you have to place it right after the chmod/chown command. One of the easiest ways is to use the find command to select the files and then run the chmod command with the -exec switch. Basic Syntax of CHMOD Recursive.
The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux. This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command to change the access permissions of files and directories.
Apply chmod 755 to directory and sub-directories only (excluding files). Try to be very specific on giving the all rights to all files and directories. So, to see a list of files in your home directory, you can execute:.
Whoever has `write' permission can create and delete files in that directory;. Sudo find directory -type d/f -exec chmod privilege {} \;. In other words, they can run the ls command to list contents of the folder/directory.
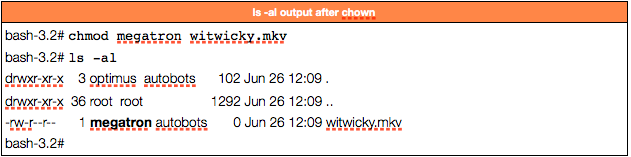
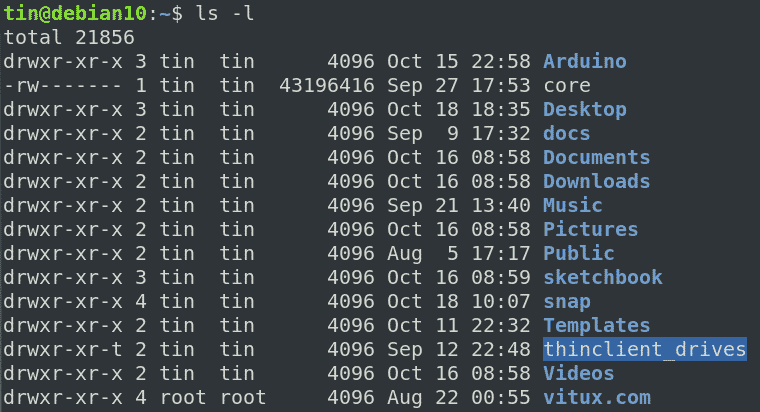
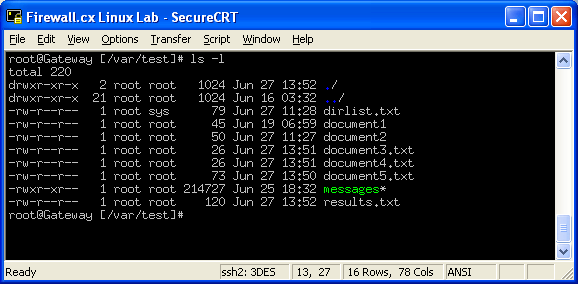
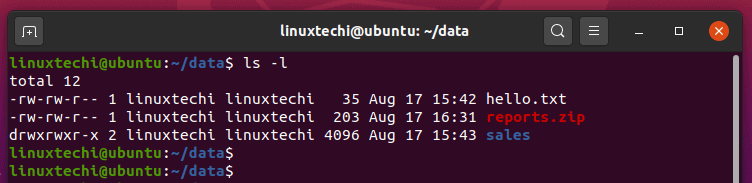
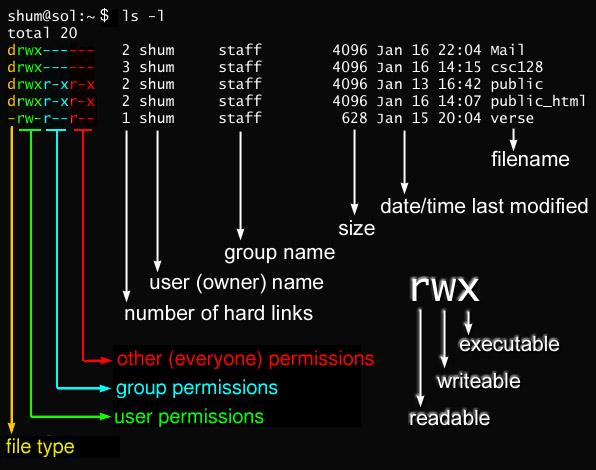
Following is a sample of ls -l command output. I have a number of files in this directory and I need to change permission from 0777 to only if that file has 777 permissions. Run Chmod separately for files and directories If you are a Linux user, you have probably heard about the console app chmod.
See chmod's man page for details. In this article, we’ll explain how to recursively change permissions of files and directories. As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory.
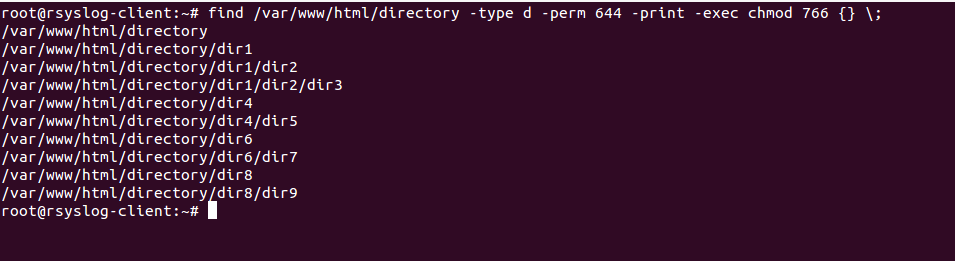
Yes, very right that the -R option in chmod command makes the files/sub-directories under the given directory will get 777 permission. Types of permissions which we will be changing using chmod command :. Find directories and change mode to 755 $find /home/james -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;.
To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions. File/Directory permission is either Read or Write or executable for either user or group or others. Linux - Solution 1:.
Specify whether it is searching for a directory -type d or a file -type f. Use chmod -R 755 /opt/lampp/htdocs if you want to change permissions of all files and directories at once. Chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems.chmod stands for change mode.Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory.
To change file access permissions you need to use the chmod command. How does chmod work?. Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions.
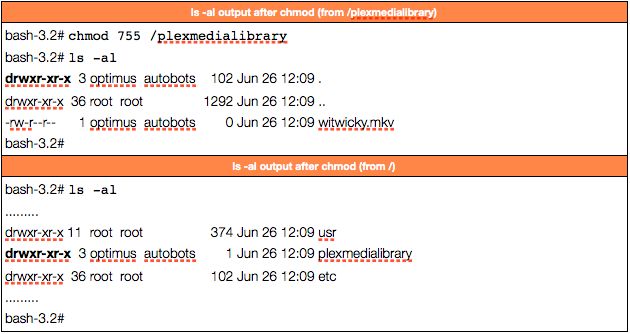
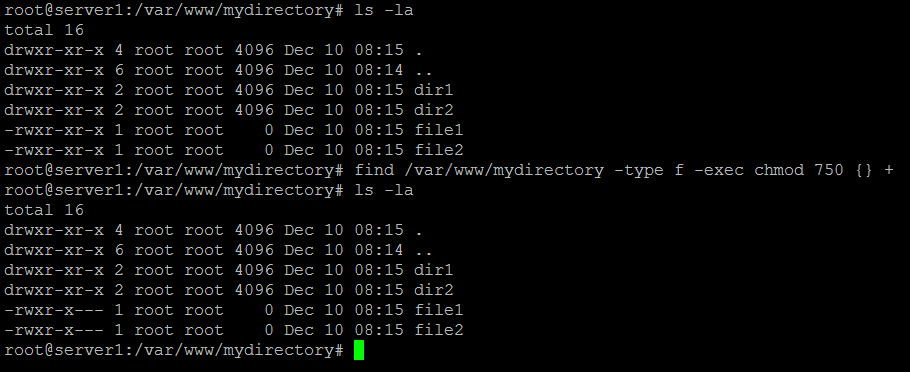
How to chmod files only on Linux There are several ways to apply a chmod to files recursively on Linux. Now, to verify if the permission is applied successfully, navigate to the “files” directory using the “cd” command and then run the “ls –l” command.From the following input, you can see that the permissions have applied successfully to all the files under the parent directory. The default umask value is subtracted from the overall file/directory default value.
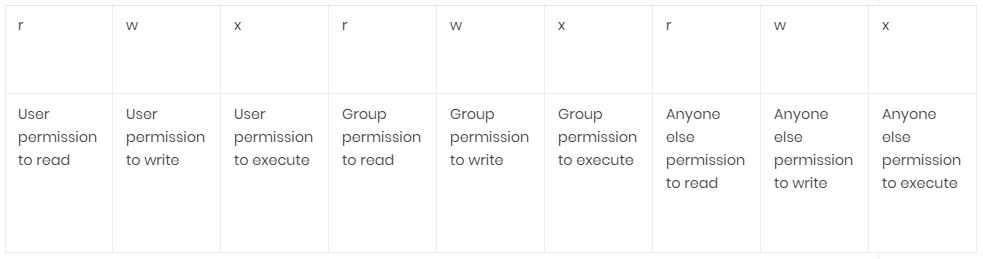
Chmod Modifies File Permissions. If the number of files you are using is very large. In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users.
Change File Permission with Find. You can also create a directory and set permissions at the same time. How to set chmod for a folder and all of its subfolders and files in Linux Ubuntu Terminal ?.
To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option. In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images.
To create directories in Linux, you can open Terminal and use the command line with the mkdir command. In this tutorial, we will show you how to change file permissions recursively with chmod and find command in Linux. Chmod -R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree.
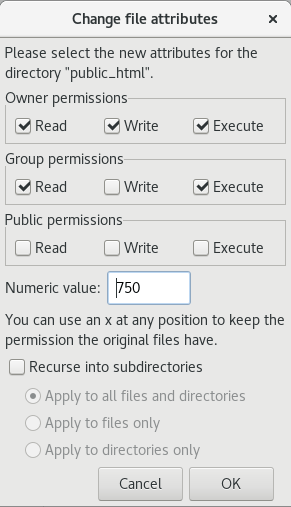
The format of the command is chmod XXX -R directory-location. $ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions. Set the file privilege with the chmod command using the numerical or symbolic mode.
Using symbols (alphanumerical characters) using the octal notation method. The command executed here is chmod 777 -R home and it gives 777 permission to the folder home itself, also to all of the files and sub-directories inside this folder. X Permission to execute the file, or, in the case of a directory, search it.
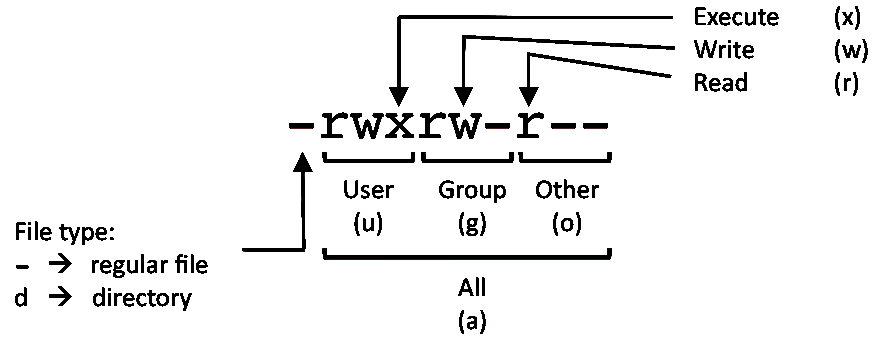
If you ever need to say it out loud, just pronounce it exactly as it looks:. Take a look at this example:. There are three sets of permissions.
Find ./mydir -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;. Whoever has execute permission can access a file or subdirectory of known name. Stand up and be counted as a Linux user!.
Chmod -R 755 can change the permissions recursively but it will change same permissions for everything, folders,subfolders and files. The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation. If you have a number of sub-folders and files within the SHARE directory, and you want the permissions to apply from the parent object (the containing folder) to the child objects (the sub-folders and files), you must use the -R (recursive) switch so the same permissions are applied all the way to the deepest folder, contained within the parent.
The chmod command has a nice shortcut for setting the executable bit only on directories, like so:. The following screenshot shows the execution of the command on a Linux Environment. I tried using ls -Rd * to see if that would list all the direcotories (thinking I could pipe it to chmod command) and it only lists the directories in the current directory, it doesn't recurse through.
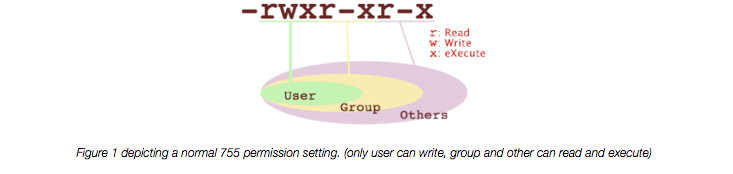
This type of restriction is useful for effective file/folder management, securing system and providing a level …. User can read, write, and execute;. In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories).It is also used to change special mode flags.
It takes the following syntax:. Yesterday I did something stupid which I today realised. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else.
The request is filtered by the umask.The name is an abbreviation of change mode. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. /root# chmod o-rwx * .* This supposed to remove read, write and execute permissions for the world on all files in the current directory (/root).As soon as I did this, screen behaved weird, I couldn't run commands as a non-root user, and ssh refused to work unless I logged in with root.
Ls ~ For Further Information. To use chmod, you need to know about access modes.Each file on a Linux system has nine access modes (or settings) that determine exactly who can. As you might remember, the default file permission value is 0644, and the default directory’s is 0755.
Use find /opt/lampp/htdocs -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;. Read permission on a directory gives you the ability to lists its content. In linux terminal, to see all the permissions to different files, type ls -l command which lists the files in the working directory in long format.
Once you create a new directory in Linux, then you can change permissions and create folders within the directory. Change into the directory with cd, before you run the find command. This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories.
This permission give you the authority to open and read a file.

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
Linux Chmod Directory And Contents のギャラリー

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

How Do Linux File Permissions Work

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
Modifying Linux Unix And Mac File Permissions Drupal Org
Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
What Is Chmod How To Use Chmod For Wordpress File Permissions

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Linux Mac And Unix File Permissions Part 1 Steven Barrett Co Uk

Chmod How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Youtube

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

14 Permission And Modification Times
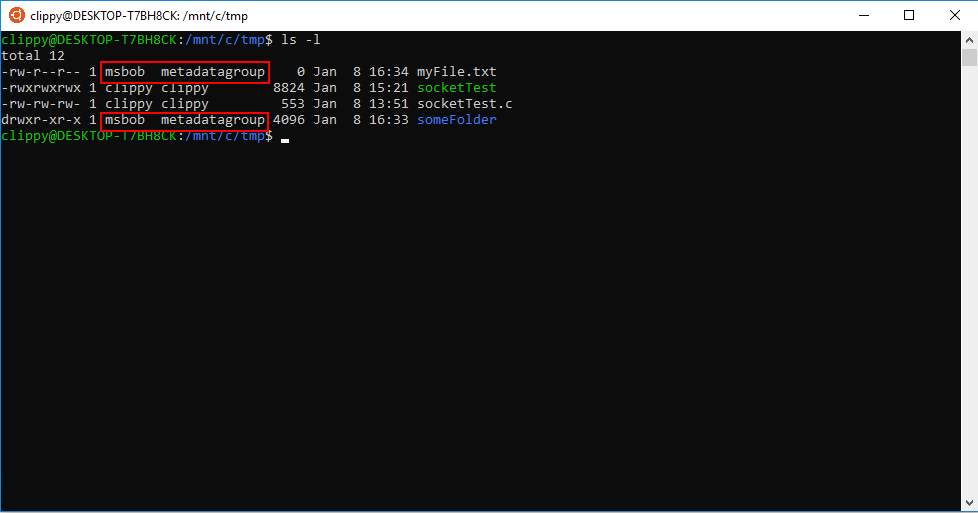
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
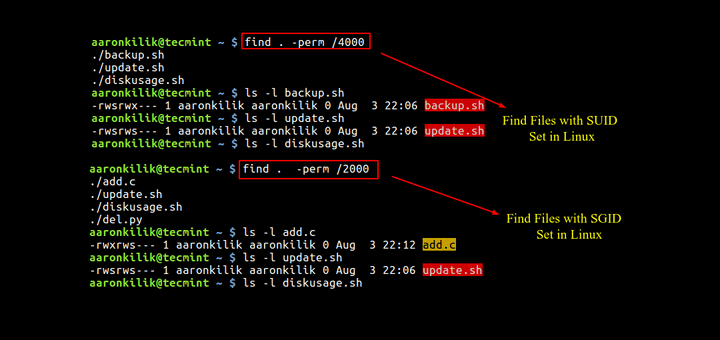
How To Find Files With Suid And Sgid Permissions In Linux

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

How To Modify The File S And Directories Permission In Linux Vasanth Blog
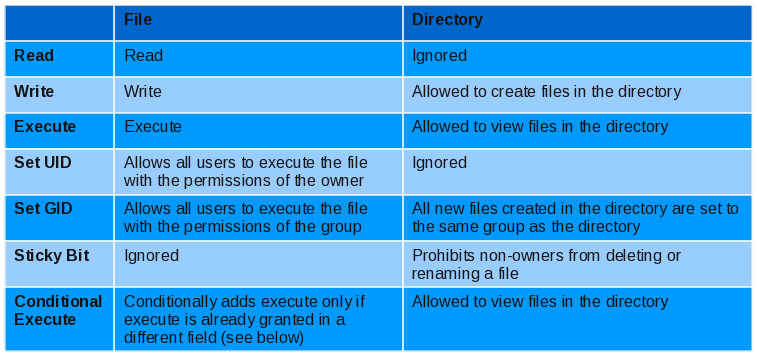
Unix Linux Filesystem Permissions 101

Linux Command Line Cheatsheet

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux
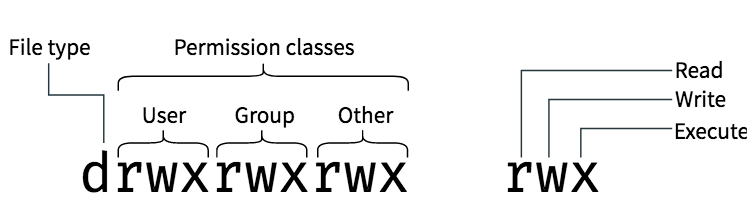
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Sep Towards Data Science
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsmtof5oge8os R2lzc9s8y8xkmcm3kyhtt M Kqujtci7flb3h Usqp Cau

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Common Bash Commands
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Setting File And Directory Access Permissions Plesk Obsidian Documentation
Linux Permissions Explained Linux Hint

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

File Permissions Suid Sgid Sticky Bit Acl Nmcli Ssh And Nmtui Tools For Rhcsa Unixmen
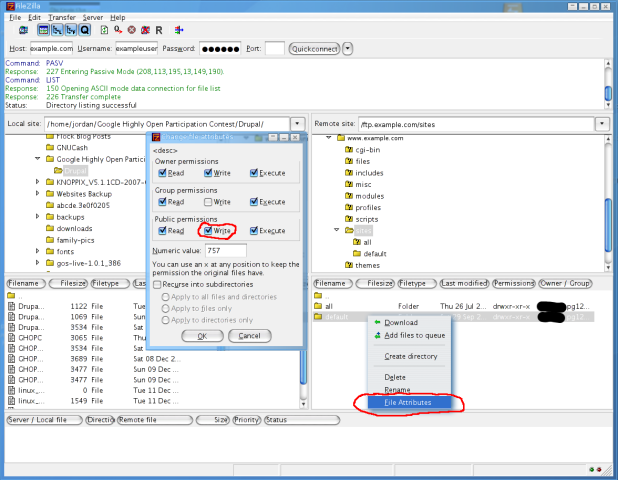
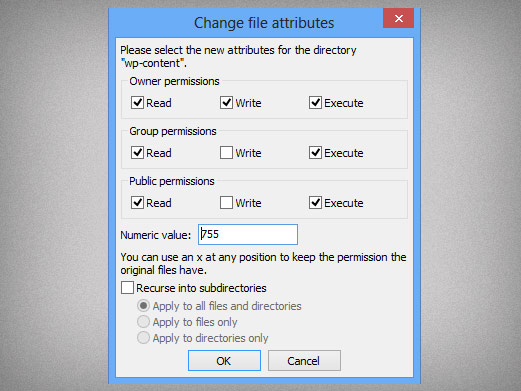
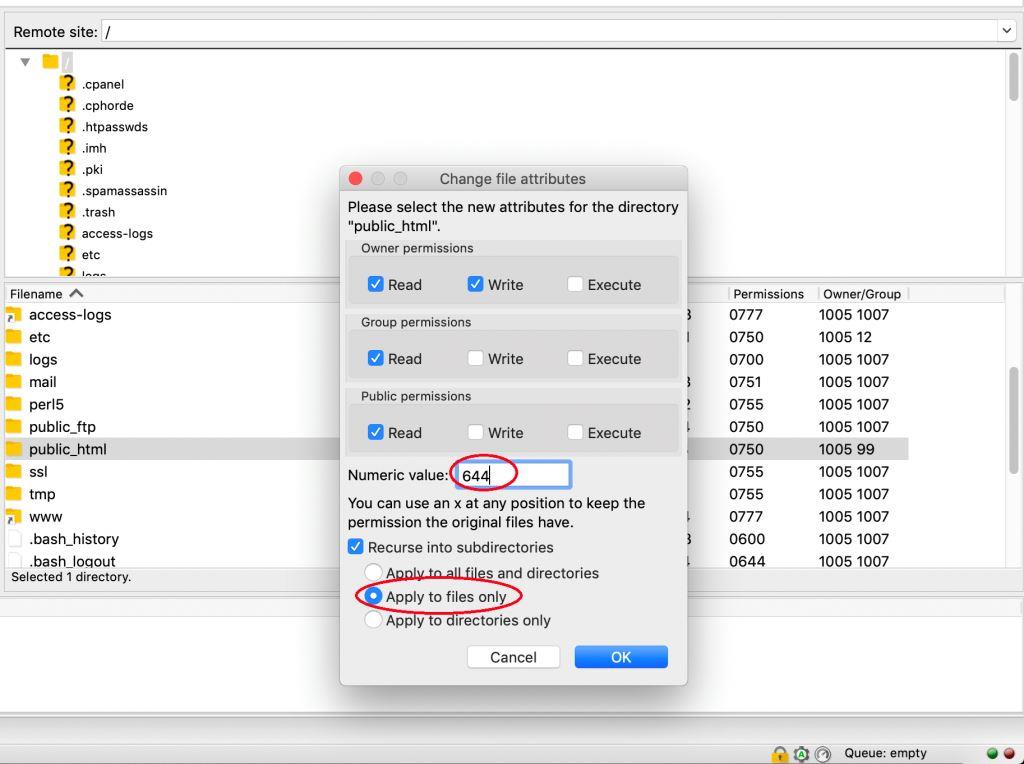
Change Permissions Of Files And Folders In Filezilla In Your Linux Hosting

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint
Linux File Folder Permissions

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Understanding And Setting Changing Access Privileges On Unix Linux Files And Directories Mode Bits Permissions And Alternative Access Methods Explained Cloud Insidr

A Note On Linux Directory Structure Users Permissions Codeproject

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut
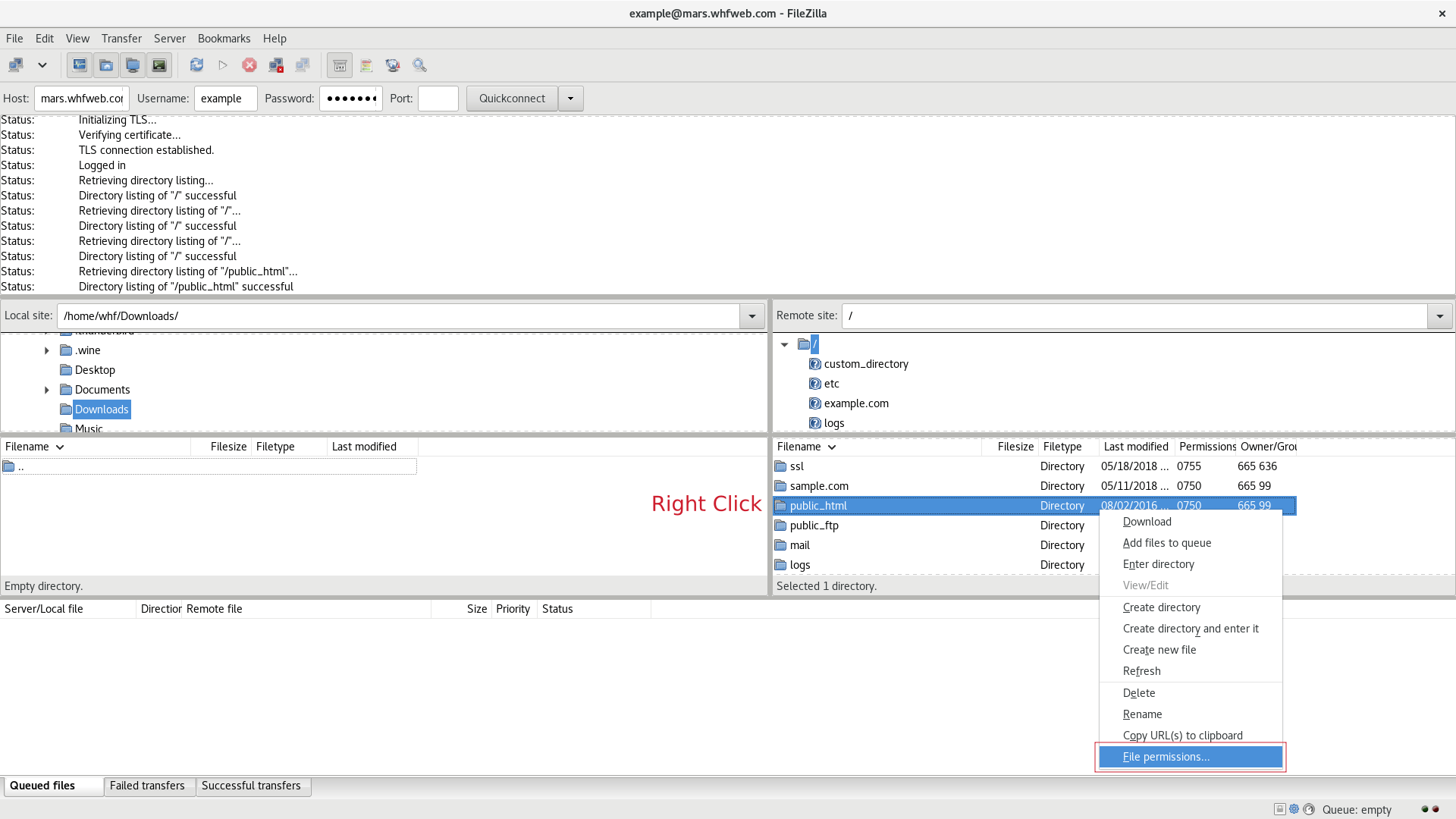
Change Permissions Of Files And Folders In Filezilla In Your Linux Hosting

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
Linux Command Cheat Sheet

Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Wordpress File Permissions The Guide To Configuring Secure Website Web Server Permissions Security Boulevard

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
Assign Read Write Access To A User On Specific Directory In Linux

Linux Concepts File Directory Permissions Hari S Technical Space

How To Reset Website File Permissions From Command Line Vi Wickam Online Expert

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

How To Fix Folder And File Permissions In Wordpress
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Chmod Wikipedia

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
How To Assign The Correct Permissions To My Prestashop Files And Folders Rolige
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
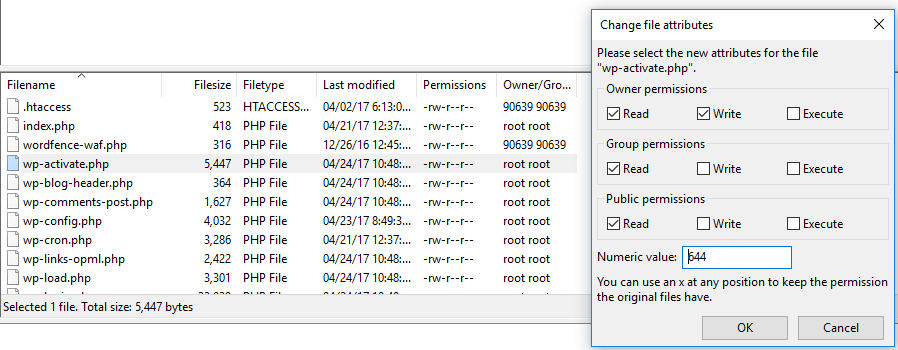
How To Quickly Fix The File And Folder Permissions Error In Wordpress Elegant Themes Blog

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs9h1s9aymhgxuiwaruv5svj Iw49oju6dx0zyl3syy0y4ft3ya Usqp Cau
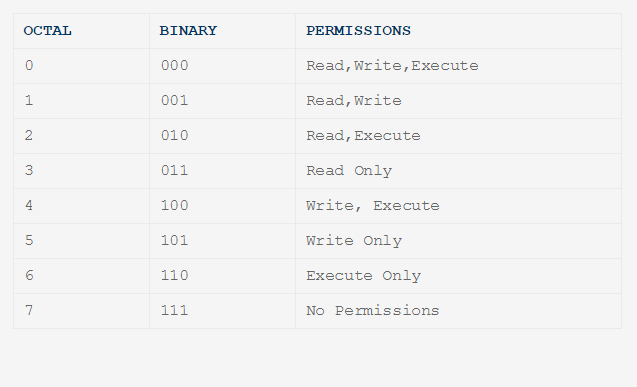
Chmod Directory Read Write And Type

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

How To Copy Files Using The Install Command On Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gct I9jvgnhaxowmpzpaajfkfizchmnvqt Bi Nz3ljrxwqpkb8l Usqp Cau

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

A Note On Linux Directory Structure Users Permissions Codeproject

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example




