Chmod
To add read and write for user, without affecting any other permissions (e.g.

Chmod. This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. The first element of the list must be the numeric mode, which should probably be an octal number, and which definitely should not be a string of octal digits:. This is a tutorial that teaches the UNIX ®/Linux ® chmod command.
$ chmod u+r,g+x filename 3. Chmod command is used to set file permission in linux/unix system. Chmod +x or chmod a+x ('all plus executable bit') makes the file executable by everyone.
Sets the permission for owner, group and others with octal values , 4 for read , 2 for write , 1 for execute and. This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. I’ll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod -r.
Modes determine who can read, change or execute a file. To remove the write permission for all other users, we run:. Chmod command is used in two ways :.
Returns the number of files successfully changed. (Modes determine who can read, write, or search a directory or file.) Users with read access to SUPERUSER.FILESYS.CHANGEPERMS (a UNIXPRIV class profile), can use the chmod command to change the permission bits of any file. To change the permissions of a directory, we run:.
$ chmod u=rw,g=r,o= birthday.cgi In this file example, sets read and write permissions for user and group:. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories.
The tutorial has been tested with Mozilla version 1.8 under Linux. Chmod stands for Change Mode and is a command often needed for installing scripts (CGI, PHP etc.) on a UNIX server, after uploading the file (with FTP) you may need to change the permissions.Basically it tells the server who can make what changes to the file or folder, i.e. The chmod() function changes permissions of the specified file.
One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users. Basically, it allows or disallows modifications of the file.
It presumes that you already know how to use the ls command to list the contents of a directory. In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories). Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links.
If you are assigning same permission then it won’t show any output. How‐ ever, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions.
In this method, the chmod command takes flags or symbols which represent the owner, group, others or all users ( u, g , and o) in the syntax. Using Options with chmod and chown Commands. You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unix-like systems such as linux or BSD.
This would grant all users and user groups with read and write access to your file, as well as allow all users to execute the file. Chmod LIST Changes the permissions of a list of files. Chmod 777 is one of those file control mechanisms.
These flags are called file permissions or modes, as in "mode of access." The command name chmod stands for "change mode." It restricts the way a file can be accessed. (O)thers can read, can't write and can execute. From one to four octal digits Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros.
This is not a problem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. Chmod u+x will made the file executable for your user (it will only add it for your user, though it may be already executable by the group owner, or "other"). This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command to change the access permissions of files and directories.
$ chmod 755 -R directory_name $ chmod 755 -R /home/linuxtechi/data Example 3) Assign permissions using text notation. If you do this to a directory, it makes the directory searchable, instead. You can change file permissions in this format:.
$ chmod a-x myscript.sh Adds read and execute permissions for everyone (a):. Another way of assigning permissions is by using the text notation. Chmod 755 Chmod 755 (chmod a+rwx,g-w,o-w) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute.
To give write permissions to everyone, execute:. DESCRIPTION chmod changes the access permissions or modes of the specified files or directories. However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file.
Change permission for all roles on a file/directory. The chmod command with the -R options allows you to recursively change the file’s permissions. Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, which can be either an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new permissions or a symbolic representation of changes to make, (+-= rwxXstugoa).
Please note the warning in the chmod with sudo section and the Warning with Recursive chmod section. In this article, I’ll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command. Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
Chmod permission directory name To change the permissions of a directory with its files and sub-directories recursively. There are three sets of permissions. Chmod means ‘change mode’ and it changes file or directory mode bits (the way a file can be accessed).
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to leave a comment. Umask is a 3 digit octal number. One of the most popular options that you can combine with chmod and chown is -R (Recursive).
One component can be computed by adding up the needed permissions for that target user base. Using octal value & position:. Chmod clears the set-group-ID bit of a regular file if the file's group ID does not match the user's effective group ID or one of the user's supplementary group IDs, unless the user has appropriate privileges.
But it will show the output only if there is any changes in permission. Recursive chmod with -R and sudo. CHMOD is listed in the World's largest and most authoritative dictionary database of abbreviations and acronyms The Free Dictionary.
Back to Dave Eisenberg’s Home Page. How to use chmod?. On Unix-like operating systems, a set of flags associated with each file determines who can access that file, and how they can access it.
Chmod is a command in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that allows to change the permissions (or access mode) of a file or directory. In contrast, chmod ignores symbolic links encountered during recursive directory traversals. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links, since the chmod system call cannot change their permissions.
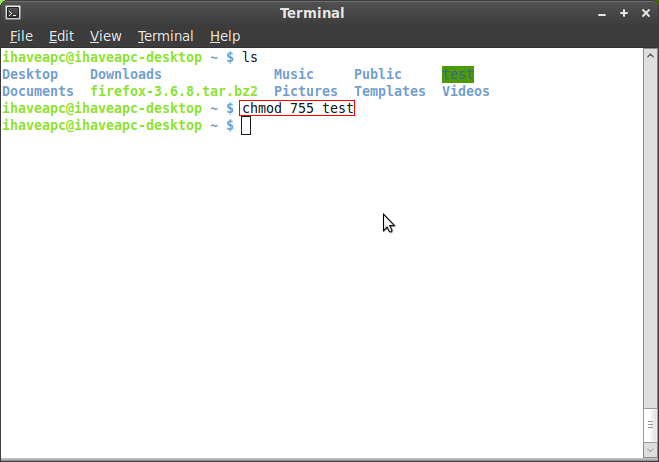
To change the permissions — or access mode — of a file, use the chmod command in a terminal. $ chmod u-rx filename 4. You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once.
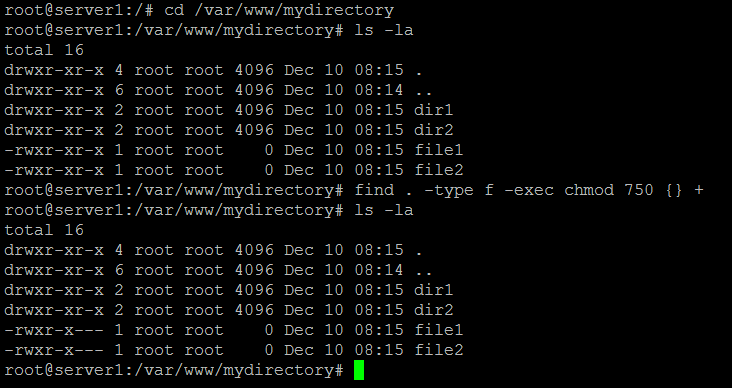
Sooner or later in the Linux world, you will have to change the permission on a file or directory. The permissions are as follows:. To recursively set permissions of files based on their type, use chmod in combination with the find command.
Chmod ( Change Mode ) is a command line utility in Unix , Linux and other Unix like systems to change the read, write, execute permissions of a file for owner , group and others. Following example removes read and write permission for the user. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders.
How to use chmod?. If you need to change a file permission, use the chmod command. In Unix-like operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file.
The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. Chmod - Unix, Linux Command - chmod - To change access permissions, change mode. Option is an additional command to change the output of a command.
The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to be. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. Chmod is a command used to change those file permissions and controls in terminals.
This Linux option allows you to change permissions or owners of all files and subdirectories inside a specific directory. Group permissio view the full answer. With great power comes great responsibility, and there’s no denying that the chmod command is an extensive and powerful.
This website has a very useful little grid checkbox thing, whereby you can tick the options you want and it gives you the command:. Introduction Multi-user systems, such as Linux, require setting up and managing file permissions that ensure only authorized users have access to files they are supposed to. There are 3 types of access level permission which unix gives.
This is not a prob‐ lem since the permissions of symbolic links are never used. Man chmod man ls A variable called `umask' is used as a permission mask for all newly created files and directories. $ chmod -c 755 file.txt mode of 'file.txt' changed from 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) to 0755 (rwxr-xr-x).
I.e., you can list the contents of a directory that you have +x. The request is filtered by the umask. Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions.
Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits. What is chmod ?. Looking for online definition of CHMOD or what CHMOD stands for?.
Use comma to separate the multiple permission sets as shown below. Chmod Modifies File Permissions In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions. Chmod command with argument -c also do’s the same thing as Verbose output (i.e.
The name is an abbreviation of change mode. More of a permission mechanism though. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;.
(G)roup can read, can't write and can execute. For more information, including octal specification of permissions, refer to the Unix User's Manual pages for chmod(1) and ls(1). Chmod g-w mydir chmod o-w mydir chmod g+x mydir chmod o+x mydir.
In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership. Chmod - What is it?. To change all the permissions of each file and folder under a specified directory at once, use sudo chmod with -R.
The name is an abbreviation of change mode. $ chmod ug=rw /var/www/html/data.php. It is also used to change special mode flags.
By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux. $ chmod u+x filename 2. $ chmod a+rx pager.pl Next, sets read and write permission for user, sets read for group, and remove all access for others:.
Chmod stands for “ Change Mode ” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system. The mode parameter consists of three octal number components specifying access restrictions for the owner, the user group in which the owner is in, and to everybody else in this order. Can the script only read the info, or can it write information as into it as well.
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. In contrast, chmod ignores symbolic links encountered during recursive directory traversals. Understanding the Linux systems helps make your system secure by restricting access to your files.
However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. 0644 is okay, but "0644" is not.
Add multiple permission to a file/directory. Following is a sample of ls -l command output. This is equivalent to the command sequence:.
However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file. For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone:. To change the permissions of multiple files and directories with one command.
Description chmod changes the access permissions, or modes, of the specified file or directory. Below is the command's general structure:. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions.
This is done with the chmod command. Remove permission from a file/directory. Chmod go-w+x mydir This denies group members and others the permission to create or delete files in mydir (go-w) and allows group members and others to search mydir or use it in a path name (go+x).
Additional restrictions may cause the set-user-ID and set-group-ID bits of MODE or RFILE to be ignored. To view these online, enter. There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022.
To remove the write permission for others for file2:.
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsuqrd7yr237u Am8msiqf70j96klzxefjagdqqwjyc32uhwnrw Usqp Cau
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

When Sudo Chmod 755 Library Tomcat9 Bin Sh Occurred An Error Stack Overflow
Chmod のギャラリー

Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Sep Towards Data Science

Chmod 777 Comic Dzone Security

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Chmod Command Tutorial How To Recursively Set Permissions In Sub Folders

Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather
Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Common Bash Commands

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Devrant A Fun Community For Developers To Connect Over Code Tech Life As A Programmer

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Explaining The Difference Chmod X And Chmod A X Youtube

Chmod 755 Livecoding Foxdot Python Youtube

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Solved 1 Using The Touch Mkdir Chmod Command Create T Chegg Com

How To Add Chmod X On A File From Right Click Menu Service In Mac Super User

14 Permission And Modification Times

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex

How To Use Chmod Change Mode Repair Your Pc Now

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
Solved This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Use Chegg Com

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Bash Chmod U X Problem In Case Statement In Shell Script Ask Ubuntu
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Chmod Not Working Q A Dataquest Community

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up

What Causes Chmod To Not Work On An Ssh File In Osx Ask Different

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
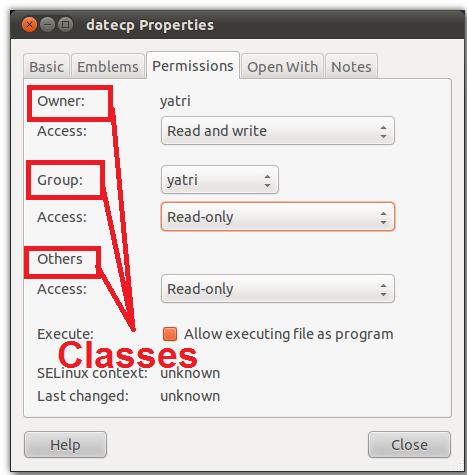
What Is Chmod 777

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Explain Absolute And Relative Permission Using Chmod Linuxteach

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
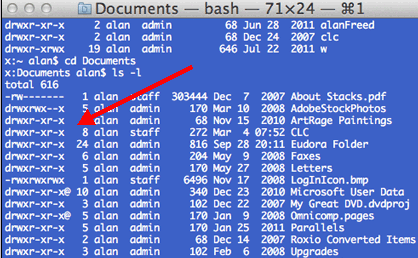
Chmod Unix Article About Chmod Unix By The Free Dictionary

Permissions Reverting From Executing Chmod By Mistake Ask Ubuntu

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Chmod Wikipedia

This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Hongkiat

How To Use The Terminal Chmod Command Demystified And Put To Use Youtube
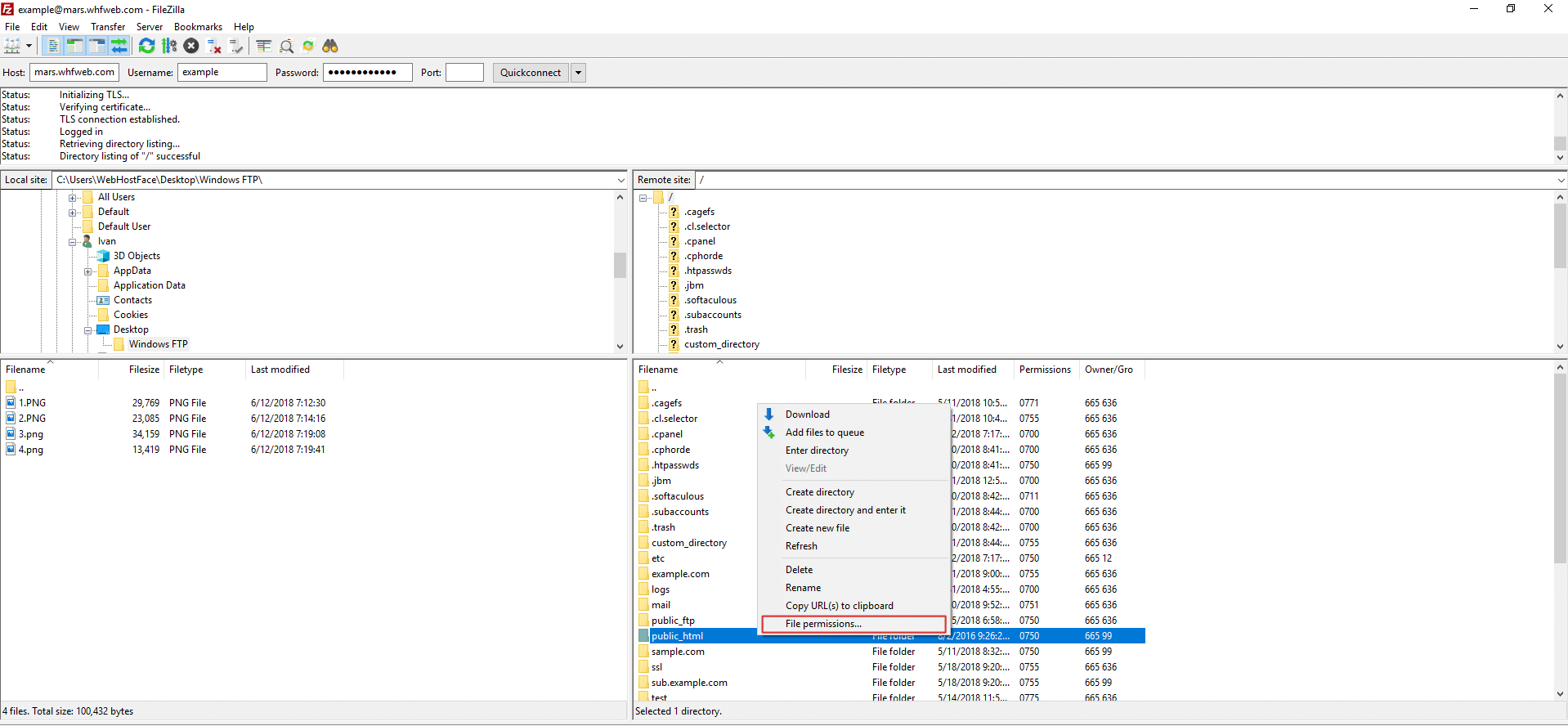
Change Ftp Permissions With Filezilla On Windows Computer
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau

14 04 Chmod Not Working In A Non Super User Ask Ubuntu

Xampp On Windows 7 Set Chmod Stack Overflow
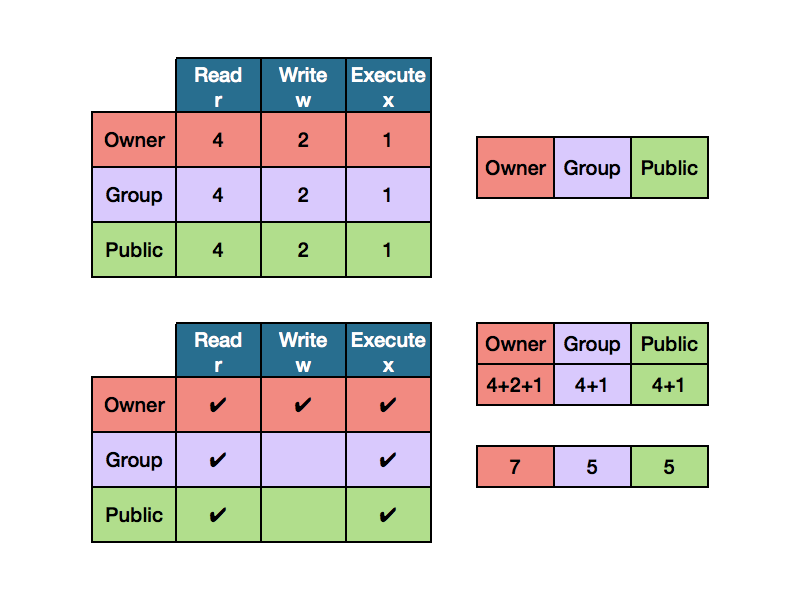
Chmod Tutorial This Is A Quick Alternative Tutorial On By Ryan Morrison Medium

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
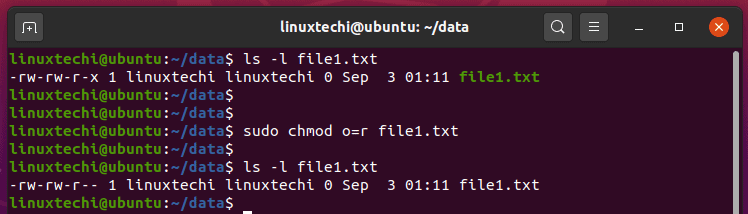
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

Linux And Unix Chown And Chmod Command Security Problem Illustrated Nixcraft

When Sudo Chmod 755 Library Tomcat9 Bin Sh Occurred An Error Stack Overflow

Ownership And Permissions
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

Pdf Chmod Cheat Sheet Sunny Yiu

Chmod X Windows Nativeyellow
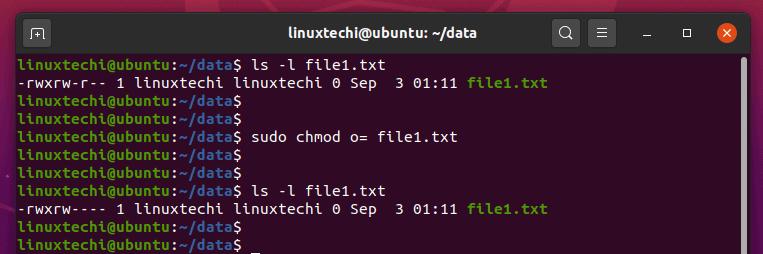
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux

This Chmod Calculator Makes Creating Chmod Commands A Cakewalk Hongkiat

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Chmod Command
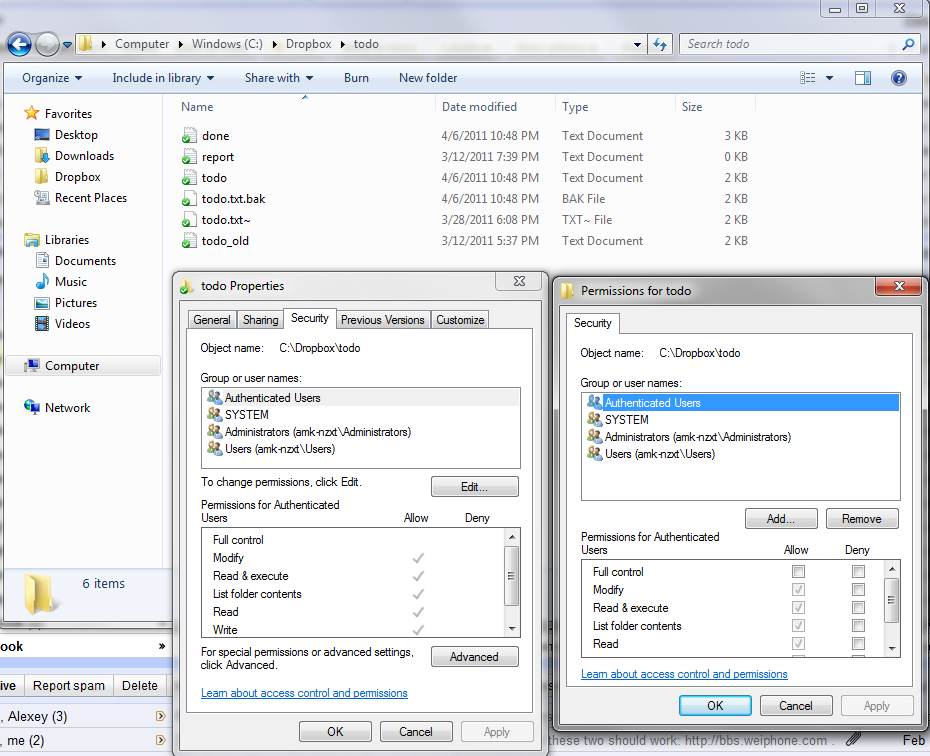
Permission Denied For Chmod Cygwin On Windows 7 Doesn T Play Nice With Files In Dropbox

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

What Did We Do When We Were Chmod 777 Develop Paper

Title Of Folders With Chmod 777 Is Not Readable Issue 36 Hukl Smyck Color Scheme Github
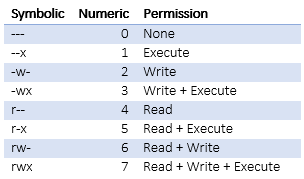
Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech

Chmod X Chmod

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Q Tbn 3aand9gct I9jvgnhaxowmpzpaajfkfizchmnvqt Bi Nz3ljrxwqpkb8l Usqp Cau

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod Command Vichhaiy Welcome

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Linux Permissions Pluralsight

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Extropia Tutorials Introduction To Unix For Web Technicians The Chmod Utility

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Network World

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux
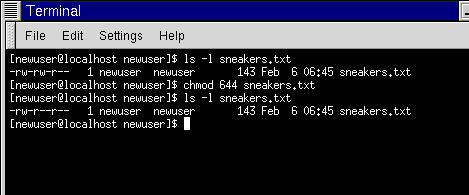
Fun With Numbers In Chmod

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro
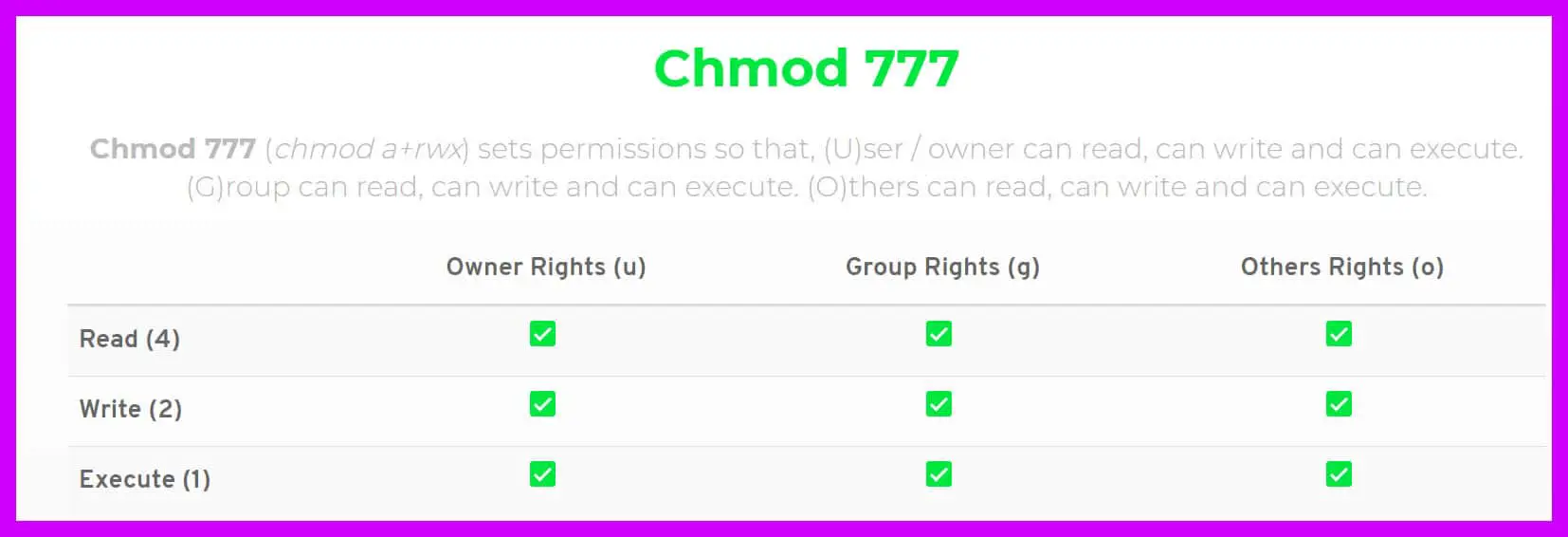
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Whatever You Knew About Chmod Is Wrong Alien Coders
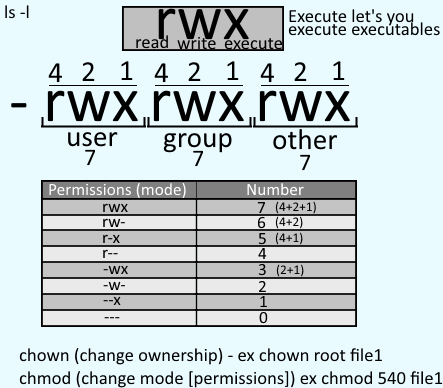
Freekb Linux Commands Chmod Change A File Or Directory Standard Permissions

Chmod 7777

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

Numeric Permissions Table Linux Chmod Command Linux Permissions




